Java Reference
In-Depth Information
CHALLENGE 5.3
For each method declared by
MachineComponent
, give recursive definitions for
MachineComposite
and nonrecursive definitions for
Machine
.
Method Class Definition
getMachineCount()
MachineComposite
Return the sum of the
counts for each component
in
components
.
Machine
Return 1.
isCompletelyUp()
MachineComposite
??
Machine
??
stopAll()
MachineComposite
??
Machine
??
getOwners()
MachineComposite
??
??
Machine
getMaterial()
MachineComposite
??
Machine
??
Trees in Graph Theory
In a composite structure, we can say that a node that holds references to other nodes is a
tree
.
However, this definition is a bit loose. To be more precise, we can apply a few terms from
graph theory
to object modeling. We can start by drawing an object model as
a
graph
—a collection of nodes and edges—with objects as nodes and object references as
edges.
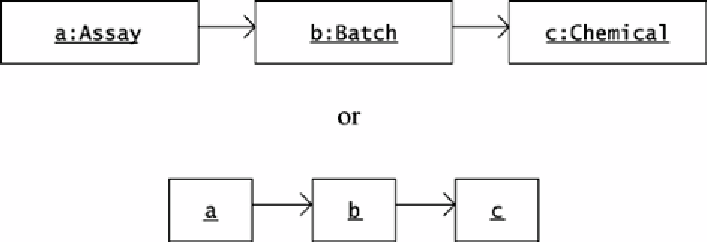
Consider an object model of an
assay
, or analysis, of a batch of a chemical. The
Assay
class
has a
batch
attribute of type
Batch
, and the
Batch
class has a
chemical
attribute of type
Chemical
. Suppose that a particular
Assay
object
a
has a
batch
attribute that refers to
a
Batch
object
b
. Suppose too that the
chemical
attribute of the
Batch
object
b
refers to
a
Chemical
c
. Figure 5.3 shows two alternative diagrams for this object model.
Figure 5.3. The two UML diagrams here show alternative representations of the same
information: Object
a
refers to object
b
, and object
b
refers to object
c
.