Java Reference
In-Depth Information
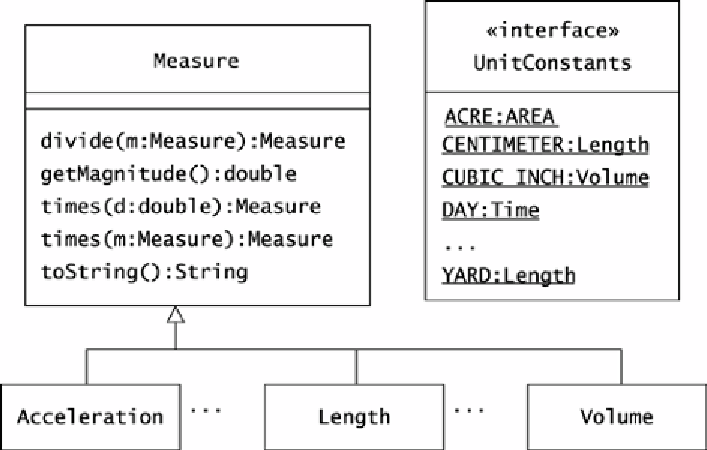
Figure 3.3. Oozinoz models units as instances of the
Measure
class, whose
subclasses represent particular physical dimensions.
A
unit
is a standard measure—a standard magnitude of a given dimension. For
example, a cubic inch is a unit of volume, and a pound is a unit of force.
The
UnitConstants
interface supplies units, and the
Measure
hierarchy supplies
dimensions for type checking. For example, the
UnitConstants
interface
supplies a
CUBIC_INCH
constant whose type is
Volume
.
You can construct new instances of
Measure
by building from the units available
in the
UnitConstants
interface. For example, suppose that the cross section of
a rocket is 0.75 square inches.
Area a = (Area) INCH.times(INCH).times(.75);
The
times()
method instantiates whichever subclass of
Measure
reflects the
dimension of the new unit. The return type of this method is
Measure
, but you can
cast the result to the more specific class that represents the measure's dimension.
To convert a measure to a quantity of a specific unit, divide the measure by the unit.
For example:
package com.oozinoz.units;
public class ShowConversion implements UnitConstants
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Volume v = (Volume) QUART.times(3);
showVolume(v);
}