Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
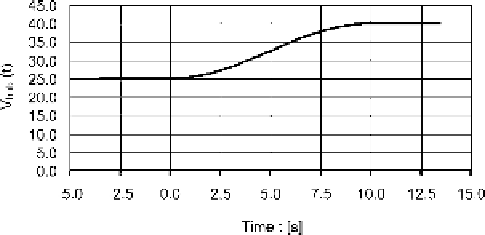
Fig. 2.13 How an extreme wind direction change varies over time (N¼50, turbulence category A,
D¼42m, z
hub
¼30m, V
hub
¼25m/s)
(
0
:
7
z
hub
for z
hub
<
30 m
L
L
¼
(as for the EOG)
21 m
for z
hub
30 m
D and
b
again as for the EOG
The way the extreme wind direction change
u
N
(t) varies over time for a return period of
N years should be calculated as follows:
8
<
0
for
t
<
0
u
N
ðÞ¼
0
:
5
u
e
;
N
ð
1
cos
ð
p
t
=
T
Þ
Þ
for
0
t
T
:
u
e
;
N
for
t
>
T
Here, T
¼
6 s is the duration of the chronological progression of the extreme change in wind
direction. The sign should be chosen in such a way that the loading gives the most
unfavourable progression. Afterwards, a constant wind direction is assumed. Figure 2.13
shows an example of an extreme wind direction change.
Extreme coherent gust (ECG)
An extreme coherent gust with a magnitude of V
cg
¼
15m/s should be assumed when
designing for standard wind turbine classes. The change in the wind speed over time is
defined as follows (see Figure 2.14):
Fig. 2.14 Rise of an extreme coherent gust (V
hub
¼25m/s)