Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where
V(z) wind speed at height z
z height above still water level
z
hub
height of hub above still water level
a
exponent
This wind profile is used to define the average wind shear force on the area swept by the
rotor. This model is based on neutral atmospheric stability. Taking a constant surface
roughness length of 0.002m, then
a¼
0.14.
Normal turbulence model (NTM)
The turbulence of the wind is represented by the energy that is transported by
turbulence eddies and for which a spectral distribution is assumed. The following
parameters are among those that characterise the natural turbulence of the wind over a
relatively short period in which the spectrum remains unchanged:
- Average value of wind speed
- Turbulence intensity
- Integral length
The values of the turbulence intensity are defined for the height of the hub. The spectral
energy densities of the random wind speed vector field must satisfy the following
requirements for the wind turbine classes of Table 2.8:
a) The characteristic value of the standard deviation of the longitudinal wind speed at
hub height (z
hub
) is assumed to be as follows:
s
L
m
½
=
s
¼
I
15
ð
15 m
=
s
þ
a
V
hub
Þ=
ð
a
þ
1
Þ
Þ
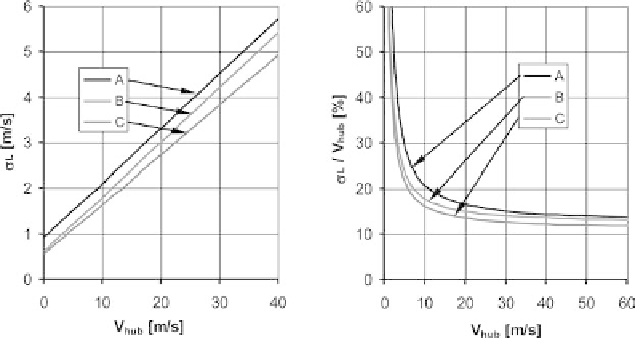
This standard deviation is assumed to be invariant over the height. Values for I
15
and a
can be found in Table 2.8. Figure 2.10 shows the standard deviation
s
L
and the
Fig. 2.10 Standard deviation of wind speed and turbulence intensity