Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
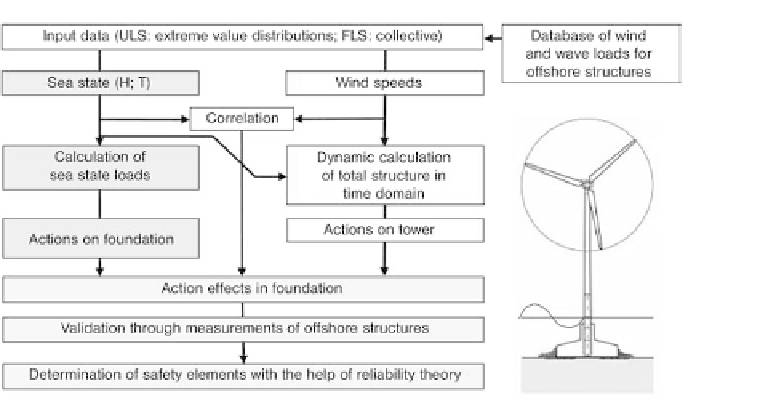
Fig. 4.16 Probability-based safety analysis
The combination factors
c
H
drawn in turn from the provisions of the GL
Guideline [11] are approximated in Section 4.6.4 as follows:
a)
c
W
and
c
W
(q
red
q
ref
)/(q
gust
q
ref
)
¼
(1.1
2
1)/(1.25
2
1)
¼
0.37 0.4
b)
c
H
(H
red
H
s
)/(H
max
H
s
)
¼
(1.32
1)/(1.86
1)
¼
0.37
0.4
Furthermore, the correlations between sea state and wind should be ascertained by way
of time series analyses taking into account the measurement data available.
Based on this, the structural safety should be evaluated with reliability theory methods
(see [25,44,45,58] and Figure 4.16).
4.6.4 Design load cases according to GL guideline
The design load cases are divided into the groups N (normal), E (extreme), A
(accidental), T (transport and erection) and allocated to the limit states U (strength
failure) and F (fatigue failure), see Table 4.4.
The significant wave height (H
s,N
) and the corresponding extreme value distribution
F
extr,3h
(H
s,N
), for example Weibull or Gumbel, are determined on the basis of long-term
statistics (e.g. scatter diagram, see Section 2.5.7) for sea states of generally 3 h duration,
see [11] 4.3.3.2 (2), (4) with 4.2.3.1.4 (2).
Return period N
¼
50 years:
H
s
;
50
¼
F
1
extr
;
3h
ð
1
1
=
N
SS
;
50
Þ
where N
ss
;
50
¼
50
365
8
¼
146 000
Return period N
¼
1 year:
H
s
;
1
¼
F
1
extr
;
3h
ð
1
1
=
N
SS
;
1
Þ
where N
ss
;
1
¼
1
365
8
¼
2920
Note: Eight sea states each lasting 3 h are possible each day.