Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
250
100
200
80
150
60
100
40
50
20
0
0
2003
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
Year
Number of people treated
Coverage (%)
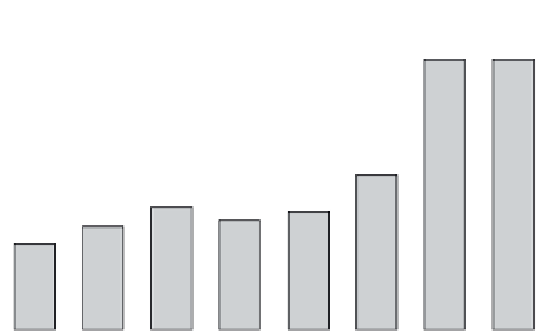
FIGURE 15.3
Number of school-aged children treated with preventive chemotherapy
for soil-transmitted helminthiasis, worldwide, 2003
2010.
e
that the number of children treated will be substantially higher than
before.
RISK OF
REDUCED ANTHELMINTHIC EF
FICACY
As a consequence of the considerable number of individuals treated for
the control of STH, an increase of the risk of development of drug resis-
tance has been evoked (
15,16
but see
17
for a recent review). However, the
studies investigating this aspect are difficult to evaluate due to the lack of
standardization and the absence of a reference threshold for drug efficacy.
WHO is seriously concerned by the possible reduction of drug efficacy
and in 2007 established a working group that, since then, is meeting peri-
odically. The working group developed guidelines on how to assess
anthelmintic drug efficacy against STH and schistosomes that standardize
the sample size, the interval between drug administration and evaluation of
the drug efficacy, and point out egg reduction rate (ERR) as the only
appropriate indicator for the evaluation of anthelmintic drug efficacy and
provide a threshold for the acceptable level of drug efficacy for albendazole,
mebendazole, and praziquantel.
18
WHO hopes that this tool will facilitate the standardization of the
study and an early identification of reduced drug efficacy should this
develop.