Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
1.2
Bounce-back
Control
Breakpoint
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
-1
4
9
14
Time (yrs)
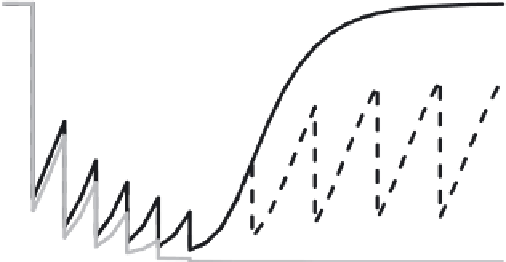
FIGURE 9.8
The effect of treatment on the dynamics of infection intensity, simulated
using Eq.
(9.9)
. In all scenarios yearly treatment is introduced for six rounds. In the bounce-
back scenario (black solid line), the treatment program is halted. If treatment is continued at
two-yearly intervals (black dashed line) then intensity bounces back, but to lower levels. If,
however, coverage levels are high enough (gray line), the break-point may be reached after
six years of annual treatment, and so intensity will not bounce back when the programme
stops. Simulations for k
¼
0.15, R
0
¼
4.5, L
1
¼
1 year, treatment efficacy 75% (black lines) and
80% (gray line).
infection. Used in combination with community-based treatment, it is the
only long-term solution for the control of STHs as well illustrated by the
outcomes in Japan and South Korea post-World War II.
Perhaps the best way to summarize needs in this area is to list a set of
key questions that surround Ascaris control by chemotherapeutic treat-
ment, and these are presented in
Table 9.1
. The answers all hinge on four
important issues identified by mathematical studies of the population
biology and transmission dynamics of STHs. The first relates to the ability
of the parasite population to bounce back to pre-control levels once
treatment ceases. The second is what factors determine the speed of
bounce-back and the third relates to the breakpoint in transmission and
where it is located (how close to zero worms per host). The fourth
concerns the expected lifespan of Ascaris eggs in the external environ-
ment, since this provides a reservoir of infection to repopulate the human
host once treatment ceases.
Bounce-back
The first two issues are fairly straightforward to address. Bounce-back
is inevitable if treatment stops in the absence of effective sewage disposal.
Ascaris populations are very resilient to perturbations. Bounce-back times