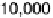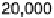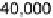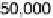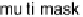Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
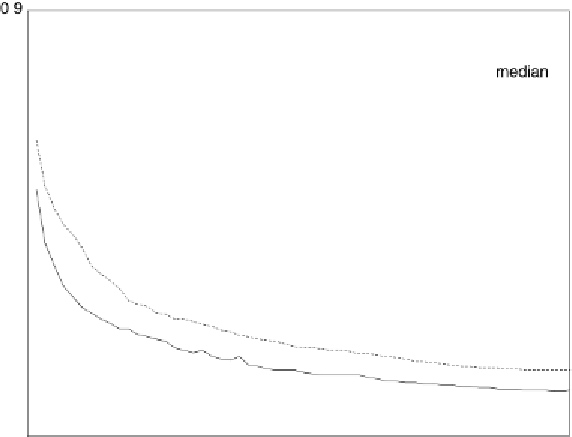
Figure 7.20
MSE plot comparing the multimask aperture, the standard aperture, and the me-
dian filter.
spatio-temporal filters. The filter kernel contains structuring elements which are
4D. That is, they exist in two intraframe dimensions of space (vertical and horizon-
tal), one interframe dimension of time, plus they have intensity values. In this case,
genetic algorithms were used to optimize the parameters of the filter over a training
set. The training set was created by selecting relatively clean parts of the footage
and pasting in noise blotches. Comparisons were made with non-training set tech-
niques such as the optimization of image quality parameters and the training set.
Procedures were always found to be superior provided that the training set was rep-
resentative of the noise and image. Further details can be found in Hamid,
16
Kraft,
17
and Marshall.
18
Figure 7.21 shows an example of old film restoration where noise “blotches”
have been removed without damaging the fine image structure.
7.6.2 Removal of sensor noise
An unsightly artifact of low-light imaging is the appearance of sensor noise. This
produces speckle on the image. Figure 7.22 shows an example of a frame taken
from low-light footage. The lower image has been despeckled using a morphologi-
cal filter. In comparison, commercial packages such as Paintshop Pro had little suc-
cess in restoring this frame.