Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Myfanwy
Alisdair
Fair
Clerical
Dark
Scotland
Wales
Jane
F
University
School
Brown
M
Manual
Harriet
Professional
England
Grey
Ivor
George
P
Jeremy
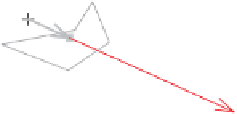
Figure 8.2
Demonstrating the vector-sum method for
George
by using the function
vectorsum.interp
.
relationship (8.2) gives
V
(
L
k
)
1
/
2
1
k
=
p
−
1
/
2
(
L
k
)
−
1
/
2
V
, it follows that
=
0
. Because
Z
k
1
L
k
Z
k
2
V
=
0
as required.
The third expression of (8.5) follows from
1
Z
0
=
1
GZ
=
1
LZ
which, on summing
the second expression over all variables, is verified to be zero.
In Figure 8.1 the row points tend to occupy the peripheral positions, so we might like
to find a more balanced presentation. The graphical representation of
Z
0
gives a visual
approximation of the row chi-squared distances (see below). We have not provided for
inner product interpretations which would require a plot of
V
and offer approximations
to
G
or
p
−
1
/
2
GL
−
1
/
2
, both of which are uninteresting. For these reasons, using lambda-
scaling to improve the figure is not an acceptable option. Furthermore, lambda-scaling
would destroy the vector-sum properties of (8.5). The remaining possibility is to scale
the row points isotropically relative to the column points. This is acceptable because the
relative chi-squared distances are unchanged. A bonus is that if we scale the row points
by a factor
p
the vector-sums become more easily interpreted centroids (see Figure 8.4).
There is a further minor advantage as follows. Suppose we ask where the centroids are
of all row points with the same categories. For example, where is the centroid of all the
=
p
−
1
/
2
1
(
L
k
)
1
/