Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
cDNA
library screening and phage display:
Display protein by phage
Biopanning for
informative antigens
Pooled sera
from patients
Probe library display for
recognized antigens
Phage array screening
Cell fractionation:
Print fractions on
multiple slides
200 400 600 80010001200
m/z
Ce l l l y s a t e
Multidimensional
fractionation in
solution or gel
Identify proteins in
informative fractions
Probe with sera
Blot 2D gels
Protein microarray:
Probe with sera
Determine sensitivity and
specificity of antigens
Protein arrays (left) or bead arrays
(right) with candidate antigens
Peptide display:
Print peptide arrays
Display peptides by phage
Probe with sera
Determine sensitivity and
specificity of peptides
FIGURE 1
Methods of antigen identification. In traditional library screening (top row), cDNA libraries from target tissue
are expressed by phage, blotted on a membrane or panned in solution, and probed with patient sera. Con
rmation of
sensitivity and speci
city requires recombinant expression of protein for ELISA analysis. Cell fractionation (second row)
involved separation of cell lysates by two-dimensional or three-dimensional separations in solution phase or in gel phase,
followed by probing with patient sera. Positive fractions are identi
rmed with ELISA.
Protein microarrays (third row) can be printed using recombinant proteins or proteins translated in situ, on slides or on bead
arrays. Because the arrays are addressable, no further antigen identi
ed by mass spectrometry and con
cation is required. Similarly, peptides (bottom) can be
printed on slides or displayed by T7 phage for rapid serum screening. (Modi
ed from reference #109, reprinted with permission.)


























































































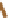









































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search