Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Note that mains fed synchronous machines mentioned here for completeness are
not used in practice. Variable speed systems are found both with induction and syn-
chronous generators.
A conventional concept is to couple an induction generator output directly to the
grid, in a system for operation at almost constant speed. A variant is the so-called
Danish Concept, where the generator has two winding systems of different pole
numbers, e.g. 4 and 6. This allows operation at two specific speeds in the ratio 2:3,
where the lower speed serves to utilize the lower wind velocities.
According to the wind rotor power characteristic the optimal operation point
shifts to larger speed values as the wind velocity increases. This shows the supe-
riority of variable speed concepts where the rotational speed is adjustable. Variable
speed systems for grid supply require adaptive devices between generator and grid;
these are generally inverters using power electronics.
In principle the same applies to systems for stand-alone operation. However, in
this case frequency and voltage regulation, and namely the reactive power require-
ments need special attention.
5.2.2 Systems Feeding into the Grid
Systems for feeding into a 50 Hz or 60 Hz network are coupled to a medium voltage
or high voltage connecting point. Under normal conditions the frequency may be
considered constant, and voltage variations are within specified values, e.g.
6%.
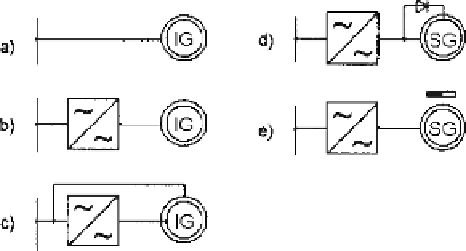
Figure 5.1 shows circuits of typical system concepts. Using an induction gen-
erator IG, the electrical machine can be directly coupled forming a system of al-
most constant rotational speed (a). Variable speed systems use a converter to decou-
ple generator speed from grid frequency, either fully fed (b) or with the converter
only for slip energy recovery (c). The latter requires a wound-rotor, slip-ring induc-
tion machine. Systems with a synchronous generator always work fully fed with a
±
Fig. 5.1
Typical concepts for generating electrical power. - using induction generator; (
a
) direct
coupling, (
b
) fully-fed, (
c
) doubly fed, - using synchronous generator, fully fed; (
d
) electrical
excitation, (
e
) PM excitation
Search WWH ::

Custom Search