Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
high demand for essential amino acids. It is impossible to cover this requirement through
'natural feed stuffs', and these productions, therefore, rely on high nutrient density imported
feed. It is difficult to compensate for this shortcoming, and more research as well as experience
is needed to develop strategies that meet all requirements regarding animal health, welfare and
production. Breeding goals emphasising this balance rather than only high animal production
must be preferred as the most sustainable long-term solution to these problems.
Feeding for animal health and welfare: the method of feeding
In addition to the composition of the feed ration and the high quality of feed, clean drinking
water should be included in the considerations regarding feeding when animal health and
welfare is a primary goal of the herd, as well as the method of feeding. In Box 7.2, an example
Box 7.2 The flat rate feeding strategy as applied in dairy
production systems in Denmark
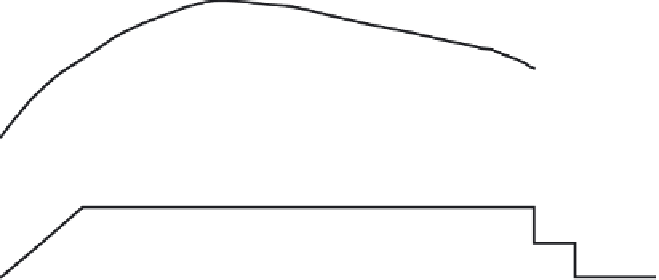
The flat rate feeding principle is illustrated in Figure 7.1. Within a herd all cows are given a
fixed amount of concentrates irrespective of daily milk yield, and roughage is fed
ad
libitum
. The length of the period with fixed amount of concentrates is typically from
calving to 24 weeks postpartum, but on some farms it lasts the entire lactation.
Kristensen and Kristensen (1998) have shown that the slope of the lactation curve is
lower in organic farming than in conventional farming, and argue that one of the reasons
is a long period with fixed amounts of concentrates and a high intake of energy from
roughage. The high persistence was especially seen for cows in the first lactation, where
the daily milk yield only dropped 0.33 kg per month from 6 to 36 weeks postpartum in
the organic herds.
Roughage quality is a very important factor when using the flat rate feeding strategy.
The variation between cows in energy demand has to be met by variation in roughage
intake.
20
18
16
Roughage
ad libitum
14
12
Reduction
according to
yield and body
condition
Rate of increase
that ensures an
increasing amount
of roughage
10
8
6
4
Concentrates in fixed amount within herd
2
0
0
6
12
18
24
30
Weeks postpartum
Figure 7.1
Illustration of the flat rate feeding strategy, based on
ad
libitum
feeding of
roughage and a fixed amount of concentrate.