Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
but it is not used. When a particular main path fails, traffic is switched to the saved backup
path for coping with the failure. Note that the computation complexity has a direct
relationship with failure spreading. Failure spreading is the condition in which the failure of a
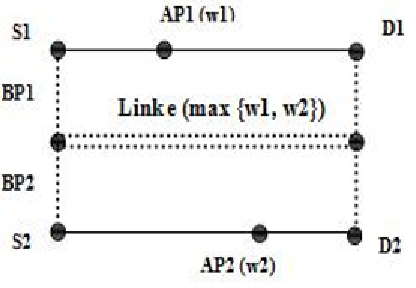
fiber can cause several upper layer failures [13]. In Figure6, for instance, consider that a link
failure occurs, where this failure will not affect the working (active) path AP1 and the
working path AP2 at the same time. Suppose that
w
1
and
w
2
are required bandwidths on AP1
and AP2, respectively. Corresponding backup paths can share bandwidth on common link
e
.
This means that the amount of the reserved backup bandwidth on link
e
(
w
1
, w
2
) equals the
maximum of
w
1
and
w
2
, not
w
1
+w
2
[17, 19].
Figure 6. Shared path protection scheme.
2.2.2.1. The 1: N Protection
The 1: N protection provides one protection channel that protects N working channels,
where N ≥ 1. In 1: N protection, there are still multiple fibers between a source and a
destination nodes but traffic is transmitted only over the working channels, while the
protection channel is kept free until a working channel fails. The failure of the working
channel causes the protection channel to automatically take over and restore data flow to the
network. Note that if multiple working channels fail simultaneously, traffic from only one of
the failed working channels is switched to the protection channel.
2.2.3. Partial Path Protection
In Partial Path Protection, when a link of any path fails, the network can use various
protection paths for sending data. Partial path protection re-uses operational segments of the
main path in path protection [11]. A collection of one or more backup paths of a partial path
protection is used for each working link so that the collection of backup paths collectively
protects all channels on the working path, where each protective path should be link-disjoint
only from the link which it protects [20]. In this way, the system can reserve protection
resources during adjusting the main path. The main distinction with path protection is that it
specifies a specific path protection for each link along the main path (i.e., each link of the
main path is protected). In case of a failure, traffic is rerouted along the protection path
corresponding to the failed link.