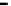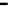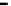Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
4000
0.004
M-fir
s
t(M=2)
M-first(M=3)
M-first with spot-checking(M=2)
M-first with spot-checking(M=3)
Credibility-based voting(random)
Cr
e
dibility-
b
ased
voti
n
g(rr1)
ε
acc
M-first(M=2)
M-first(M=3)
M-first with spot-checking(M=2)
M-first with spot-checking(M=3)
Credibility-based voting(random)
Credibility-based voting(rr1)
0.0035
3500
0.003
3000
0.0025
2500
0.002
2000
1500
0.0015
0.001
1000
500
0.0005
0
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
pd
pd
(a) Error-rate
(b) Computation time
T
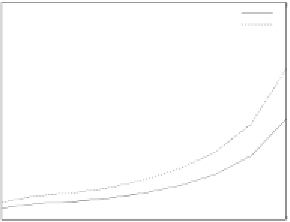
Figure 20.
M
-first voting with spot-checking vs. Credibility-based voting for defection
rate
p
d
(
acc
=0.001
,
s =0.1
,
f =0.35
,
q =0.1
,
c =1.0
,
P
up
(steady)=0.8
, random
scheduling without blacklisting).
defect and rejoin the system, which resulting in non-zero
p
d
. For example, when
p
d
=0.5
,
it doubles the computation times compared with those in the basic model.
3.3.
Conclusion
In this section, we compared the performances of
M
-majority voting,
M
-first voting,
M
-
FVSC and credibility-based voting in terms of error rate and computation time of VCs.
Through the extensive simulations, we found the following important results;
•
Error rate:
-
M
-first voting decreases error rate more efficiently than
M
-majority voting.
-
When saboteurs collude, error rate dramatically increases in simple voting
methods such as
M
-first voting. Spot-checking-based methods, i.e.
M
-FVSC
and credibility-based voting, work well in this case.
-
When
s
,
f
and
c
are large,
M
-FVSC requires huge redundancy to satisfy the
reliability condition
≤
acc
.
-
Credibility-based voting guarantees the reliability condition for any
s
,
f
,
c
and
p
d
.
•
Computation time:
-
Credibility-based voting tends to show better performance than
M
-FVSC; how-
ever, it sometimes performs excess redundant computation and degrades the
performance since it always assumes the worst case (e.g.
f = f
max
and
c =1
).
-
The computation time of credibility-based voting largely depends on the job
scheduling method.