Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
elastic, diffusive mode which diverges, whereas the intensity of the in-
elastic mode stays finite and its energy is still non-zero at the transition.
Within the simple MF-RPA theory, the critical behaviour has changed,
because of the elastic term in the crystal-field susceptibility, so that the
transition is no longer accompanied by a soft mode. The energy of the
inelasticmodeat
q
=
Q
,when
T
is close to
T
N
, depends on ∆ and on
how large the elastic term is at the transition. If this elastic contribution
is small, the energy of the inelastic mode may be so small that it be-
comes overdamped because of the influence of the critical fluctuations,
and therefore indistinguishable from the divergent diffusive peak. How-
ever, if the inelastic mode is suciently separated in frequency from
the low-frequency critical fluctuations, it may persist as a reasonably
well-defined excitation even near the phase transition.
The dhcp structure of Pr has four atoms per unit cell, so there
are four branches of the dispersion relation for each polarization. If the
hexagonal and cubic sites are decoupled, these decompose into two sets,
each comprising two modes, which may be described as acoustic and
optical, propagating on the sites of a particular symmetry. The com-
plementary excitations to those of Fig. 7.1 propagate on the cubic sites,
and their dispersion relations, also studied by Houmann
et al.
(1979),
are illustrated in Fig. 7.2. If the hexagonal sites are ignored, the cubic
sites lie on a simple hexagonal lattice, so that a double zone may be
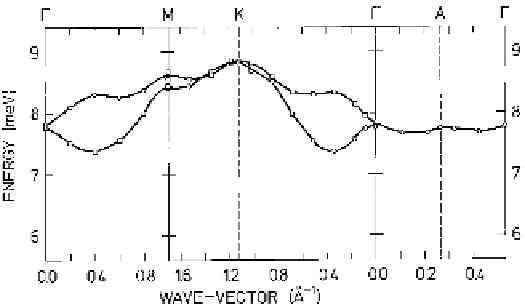
Fig. 7.2.
Dispersion relations for the excitations propagating on the
cubic sites of Pr at 6 K, plotted in the Brillouin zone of the dhcp structure.
The upper and lower branches in the basal plane are respectively the
acoustic and optical modes. The polarization vector of these excitations
is perpendicular to the
c
-axis. In contrast to Fig. 7.1, no splitting of
these branches by anisotropic two-ion coupling is observed, within the
experimental resolution of about 0
.
5meV.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search