Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Directed evolution
Circuit:
l
1
l
2
l
3
Design
Output
l
1
Tu n e
inputs
Plasmid/
genome
Constrained
library of parts
l
3
l
2
Screening and
Selection
Part activity
Optimized
circuit
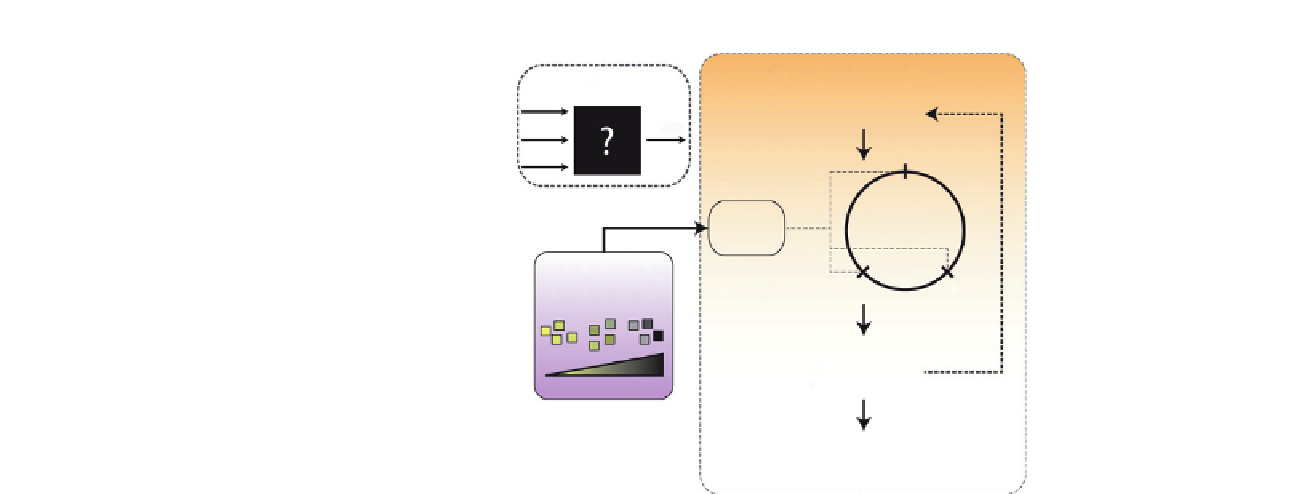
FIGURE 4.3
Constrained libraries of parts improve the development cycle of circuit optimization using directed evolution. An illustrative
circuit composed by three inputs is depicted in the figure. Directed evolution permits a rapid and exhaustive search
methodology to optimize circuit function when screening and/or selection procedures are available. Its efficiency to investigate
the vast space of solutions can be further increased if combined with biological elements that ensure differential and
reliable function.
power of MAGE, the authors optimized the 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP)
metabolic pathway to overproduce lycopene. They used MAGE to vary the translational
efficiency (through RBS degeneration) of 20 different genes previously reported to affect the
pathway, and also to inactivate four other genes that redirect the flux to competing pathways.
From as many as 15 billion genetic variants, the authors found strains, by screening for color
intensity, with up to a five-fold increase in lycopene production as compared with the wild-
type system. Indeed, the ability to rationally target key variables such that sequence variation
maps to known parameter ranges, distributed across the entire genome, in a multigene
pathways
74
performance increases search efficiency such that optimization of pathways with
large numbers of relevant genes (in this case 20) becomes possible.
'
It is worthwhile to point out that in these directed evolution experiments, the diversity and
number of rounds of selection available is limited (by the inefficiency and time-consuming
nature of transformation), but knowledge of where variation should be targeted (rational
design) combined with technologies for producing targeted libraries are used to spend the
limited diversity wisely. In fact, biological parts with well-defined sequence
activity
relationships present an effective starting material to target and mutate circuit components
and generate genetic variability that more efficiently cover the search space of circuit
functionality (
Figs 4.2 and 4.3
). Alternatively, one may invest in strategies that dramatically
expand the diversity and the number of rounds of selections by developing continuous
targeted evolution systems. Such efforts are underway in the directed evolution and
synthetic biology communities.
51
Design of Experiment Approaches
For directed evolution to be applicable, one must have a phenotype that is either
selectable or can be screened in high throughput. Otherwise, the amount of time required to
characterize the often staggering number of variants considered in a directed evolution
experiment becomes prohibitive. Although the semirational directed evolution experiments