Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
PROGRAMMING ANTAGONISTIC INTERACTIONS BETWEEN
POPULATIONS
In addition to cooperation between populations, microbial consortia have been designed
based on antagonistic interactions. Engineering of such consortia has led to the study
of ecologically and evolutionary relevant phenomena, while also serving as a platform to
advance the ability to engineer complex behaviors. Balagaddé et al. constructed a synthetic
predator
prey system consisting of two
E. coli
strains that communicate bidirectionally
using two QS systems.
25
Each strain harbors a QS signal synthase gene (
lasI
for predator
and
luxI
for prey) and a cognate receptor protein for the QS signal produced by the
other strain (LuxR for predator and LasR for prey). As such, the receptor protein in one
strain is activated when the other strain is present at sufficiently high density. The logic
of the predation, where the predator kills the prey and the prey helps the predator
s
'
survival and growth, is realized by utilizing a toxin
antitoxin pair. The predator
sQS
'
signal activates a toxin gene,
ccdB
, in the prey while the prey
s QS signal induces an
antitoxin gene,
ccdA
, which neutralizes the effect of the constitutively expressed
ccdB
in the predator (
Fig. 13.2A
).
'
(A)
Predator
Prey
P
LtetO-1
P
lux
luxR
lasl
ccdB
LuxR
P
lac/ara-1
LasR
P
lac/ara-1
ccdB
ccdA
248
P
lux
luxl
lasR
(B)
(C)
R
40
Prey
30
Predator
20
10
0
0
40
80
120
160
200
S
P
Hours
FIGURE 13.2
Engineering competition within a synthetic consortium. (A) A synthetic predatorprey system. The predator and prey
populations control each other
'
s survival and death via two different QS signals. The predator and prey synthesize 3OC12HSL
(green circles) and 3OC6HSL (orange circles) via LasI and LuxI, respectively. The signal from the predator population is
sensed by the prey population via LasR, while that from prey population is sensed by the predator population via LuxR. The
QS genes in the predator are constitutively expressed from P
LtetO-1
, and those in the prey are under IPTG-inducible promoter,
P
lac/ara-1
. The ccdB toxin gene is controlled by P
lac/ara-1
in the predator and P
lux
in the prey. P
lux
also regulates ccdA antitoxin
gene in the predator. Redrawn from Balagaddé et al.
25
(B) Typical oscillatory predatorprey dynamics observed using a
custom-made microfluidic device. Adapted from Balagaddé et al.
25
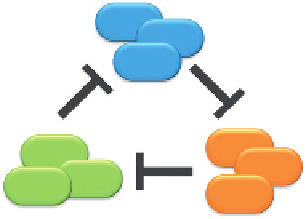
(C) Schematic of a rockpaperscissors interaction. The
colicin-producing population (P) kills the colicin-sensitive population (S). The S population outcompetes the colicin-resistant
population (R), which can outcompete the P population.