Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
As described by Gibson et al.,
6
unsuspected mutations may freely accumulate in proportion
to both the increase of the DNA size and the number of cell divisions during prolonged
cultivation.
CB has been cultivated only in
B. subtilis
growth conditions. There is no selection pressure
on holding the guest genome. One deep concern for the guest genome is fidelity at the
nucleotide sequence level of progenies. Because recent sequencing of the CB genome
unveiled little traits of insertions, deletions, and SNPS,
34
it was astonishing that large DNA
in
B. subtilis
did not suffer mutation incorporations. We are confident that genes required
for growth and photosynthesis reactions excluding plasmid-borne genes are not affected.
MITOCHONDRIA AND CHLOROPLAST: ORGANELLE GUEST
GENOMES IN BGM
Megacloning of the two whole organelle genomes, mouse mitochondria and rice
chloroplast, was implemented.
12
Their sizes, 16.5-kb for the mitochondria DNA that carries
only 13 genes and 135.5-kbp for the rice plastid carrying 128 genes, were dramatically
smaller if compared with the
Synechocystis
genome as sketched in
Figure 12.1
. Both organelle
genomes were good systems to establish slightly different assembly methods in BGM. The
domino method is a one-way cloning and the cloned DNA stays in the
B. subtilis
genome. A
retrieval method out of the
B. subtilis
genome is needed to isolate megacloned DNA for
further use. More importantly, both organelle genome DNAs were retrieved out of the BGM
genome and isolated as a circular form.
12
As illustrated in
Figure 12.4
, a Bacillus
Recombinational Transfer (BReT) method we developed
35
37
was applied. Complete
circular organelle genomes freely designed would be valuable to examine systems for direct
plastid genome delivery in plant cells. In particular, chloroplast genomes available in the
BGM vector
12
should be suitable to compare gene expression profiles with those of
Synechocystis
in CB.
234
BReT method
LPSI
LPS
oriC
oriC
X
X
terC
terC
LPS
LPS2
Genome dissection
eo
oriC
eo
neo
e
oriN
X
ne
terC
ne
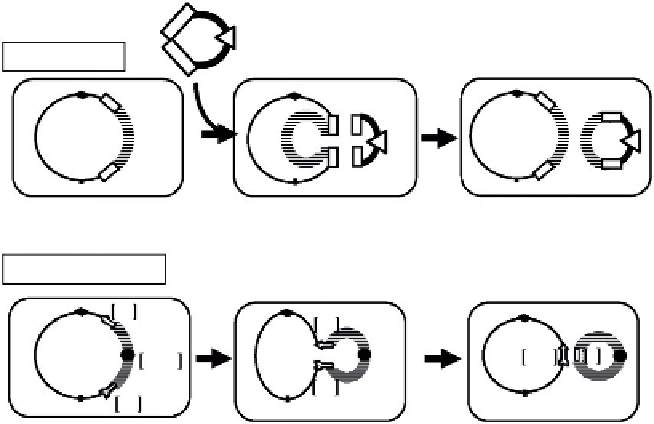
FIGURE 12.4
Genetic methods to retrieve cloned DNA out of the BGM vector. Two methods were developed for the BGM vector. Top: BReT,
Bacillus Recombinational Transfer. BReT plasmid possessing an antibiotic resistance marker (open triangle) and LPS1 and
LPS2 sequences identical to those in BGM is linearized prior to transformation. Circular BReT plasmid forms only by copy and
paste of the intervening DNA region between genomic LPS1 and LPS2 by homologous recombinatons indicated by X. Bottom:
The target part to be retrieved is designated by two DNA repeats ne and eo installed at both ends and a new origin of
replication oriN. Intrachromosomal homologous recombination between the two repeats is indicated by X producing neo and e.
The creation of neo, a complete neomycin resistance gene, allows positive selection for intervening region DNA circularized
under oriN-dependent replication.