Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
[Grows with CO
2
and light]
[Requires organic nutrients]
Convertible?
CyanoBacillus
Cyanobacterium
Bacillus subtilis
rrn
rrn
rrn
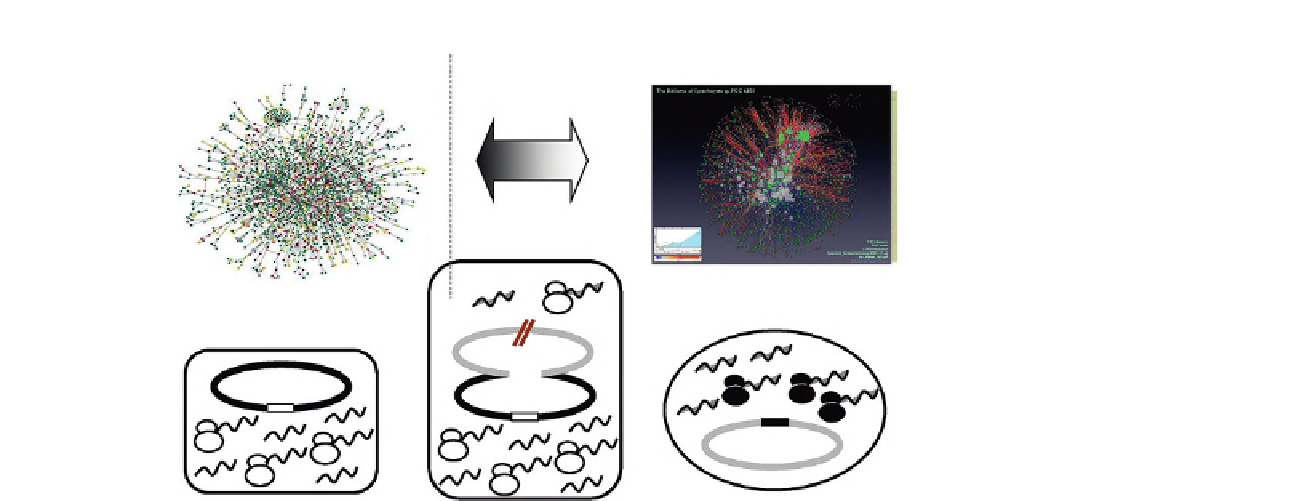
FIGURE 12.3B
CyanoBacillus: Interchangeable gene expression networks? CynoBacillus lacking only two rrnA and rrnB is schematically
drawn in the bottom middle. Gene expression and ribosomes in the host B. subtilis (left) and guest Synechocystis (right) are
altered in CB. Expression of reduced transcripts and few translated product from guest genes are described in the text.
Robust gene networks for the host and guest (top) might be exchangeable by certain factors.
25
sketched roughly in
Figure 12.3B
. These observations did not fulfill any predictions derived
from the normal central dogma scenario in which translation tends to be coupled with
transcription. The robust host gene network and the sterile guest one should be tightly
coupled with presence and absence of ribosomes, as argued below.
231
EXCLUSIVITY OF RIBOSOMAL RNA IN THE HOST
CB lacked two ribosomal gene operons,
rrnA
and
rrnB
from
Synechocystis
. The guest
rrn
operons displayed complicated roles and have raised a possible scenario on species selection
in a previously unsuspected manner. It should be emphasized that the presence of ribosomal
gene operons alone, regardless of
rrnA
and
rrnB
, did not cause any detrimental phenotypes on
B. subtilis
. They had to be deleted halfway in elongation before completing the synthesis of
the chimera genome as detailed below. The step-by-step step elongation method left many
intermediate strains that possess part of guest DNA of different regions and in different
lengths (
Fig. 12.3A
). The
rrn
exclusivity was not found until the accumulation of the
Synechocystis
genome up to 2.6 Mbp in
B. subtilis
, insert stage F of
Figure 12.3A
. At that stage,
another domino elongation always accompanied big deletions randomly from guest genome
parts already present in BGM. Eradication of the guest
rrn
A operon only, a 5.4 kbp-long DNA
segment shown in
Figure 12.3A
, solved all the stalling problems and allowed the rest of the
megacloning to be completed. Together with the same exclusivity for the other
rrnB
, these
observations strongly demonstrated that expression of guest
rrn
species turned out to be toxic
if a certain number of
Synechocystis
genes are accumulated and possibly expressed during stage
F. Toxicity might be brought in by possible formation of chimera ribosomes that should not
stand with pure
B. subtilis
ribosomes. This explanation is one of many scenarios and remains
controversial and elusive, which requires more experimental evidence.
Function of chimera ribosomes created by mixing 23 S from
E. coli
with 16 S from different
species was reported in
E. coli
, in which 16 S seems to be restricted to species closely related
to
E. coli
.
23
No experimental indication has been yet made available for chimera ribosomes
between
B. subtilis
and
Synechocystis
. Absence of guest ribosomal RNA is consistent with the