Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 12.2 Pseudo code for the active learning framework.
Based on the active learning framework presented in Figure 12.2, the
marketing learning problem can be defined as follows:
While keeping the total net acquisition cost to minimum, the goal is to
actively acquire from
S
mutually exclusive subsets
S
1
,S
2
,...,S
k
of a given
batch size
M
, such that the final classifier induced from
k
i
=1
S
i
maximizes
the profitability of the campaign. The subsets are acquired sequentially.
This is a Multiple Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) problem. The
first criterion is to improve the decisions of the campaign manager.
The positive reaction rate can be used to assess the profitability during
the exploitation phase. Higher rates indicate higher gross profit margins
and return of investments (ROI). The second criterion is to acquire labeled
instances with minimal net acquisition cost during the exploration phase.
Both criteria deal with financial utilities. Still, the two criteria cannot be
summed. We cannot represent the first criterion as total income during the
exploitation phase, since we do not know in advance how many customers
are going to be evaluated using the model. The only assumption we make
is that the instances in the unlabeled instances set used during the training
phase (
S
) and the instances examined during the operational phase are
both distributed according to a fixed and unknown distribution
D
.In
this paper, we consider the first criterion as primary and the second as














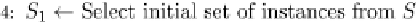


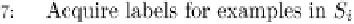



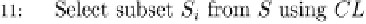






Search WWH ::

Custom Search