Java Reference
In-Depth Information
Operator Precedence
Does 1 + 2 * 3 = 1 + (2 * 3) = 7 or does it equal (1 + 2) * 3 = 9?
Operator precedence determines the order in which operators are evaluated. For example, the multipli-
cative operator (*) has a higher precedence than the additive operator (+). Therefore, the correct answer
to the previous question is
1 + (2 * 3)
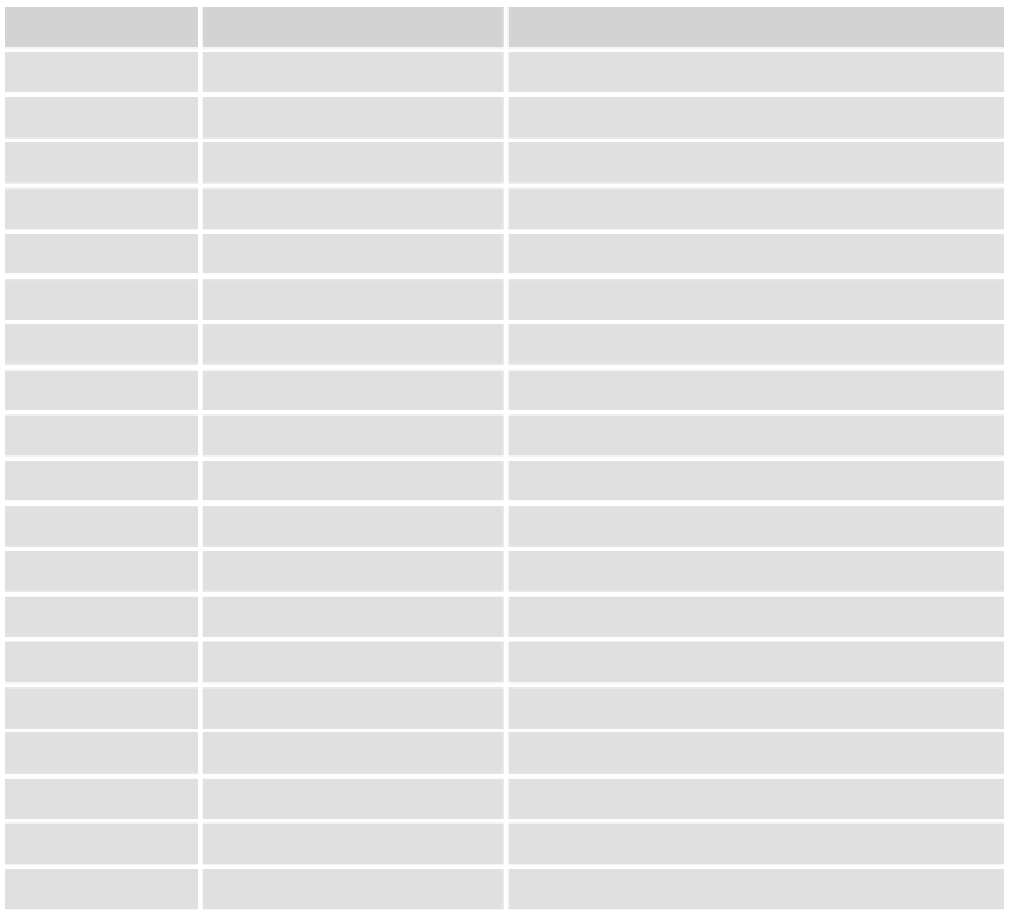
The following table lists the operator precedence in JavaScript from highest to lowest. The third column
explains whether to read 1+2+3+4 as ((1+2)+3)+4 (left to right) or 1+(2+(3+(4))) (right to left).
Operator Type
Operators
Evaluation Order for Like Elements
Member
.
or
[]
Left to right
Create instance
new
Right to left
Function call
()
Left to right
Increment
++
N/a
Decrement
—
N/a
Logical not
!
Right to left
Bitwise not
~
Right to left
+
Unary +
Right to left
Unary -
-
Right to left
Ty p e o f
typeof
Right to left
Void
void
Right to left
Delete
delete
Right to left
Multiplication
*
Left to right
Division
/
Left to right
Modulus
%
Left to right
Addition
+
Left to right
Subtraction
-
Left to right
Bitwise shift
<<, >>, >>>
Left to right
Relational
<, <=, >, >=
Left to right