Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
simulations include exponential, power law (Shaw, 1994, 1995, 1996; Gibson and
Austin, 1996) and half Cauchy distributions (a 'long-tailed' distribution) (Xu and
Ridout, 1996, 1998, 2000, 2001; Diggle
et al.
, 2002; Fink and Kofoet, 2005). A
simple 'nearest neighbour' dispersal function was used to model barley yellow
dwarf virus transmission by aphids (Chaussalet
et al.
, 2000).
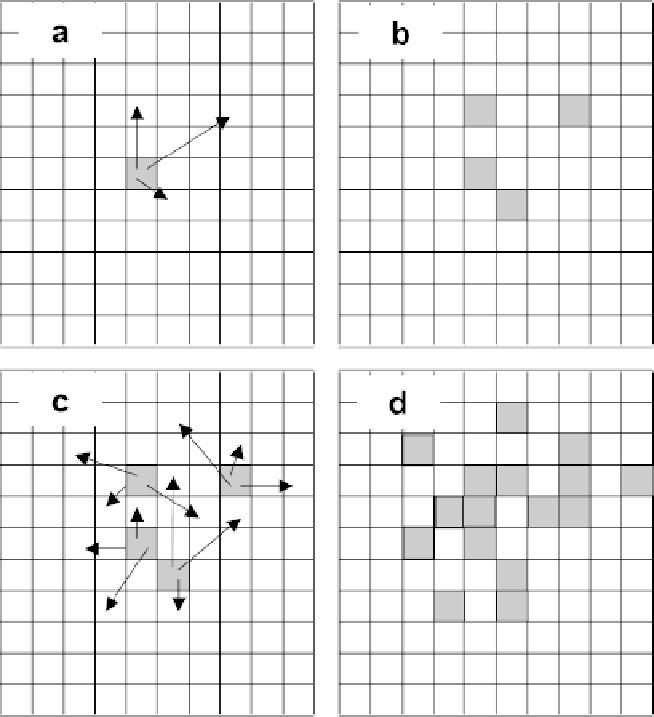
Figure 6.3. A simplified stochastic disease spread model. Grey squares are infected plants.
Plants release spores that travel in straight lines (a) to infect other plants (b) which in turn
release spores (c) to infect other plants (d).
Stochastic disease modelling suggests that
PDFs
with 'long tails' are more likely to
produce discrete 'daughter' foci separate from the main focus than exponential
PDFs
(Shaw 1994, 1995). Stochastic models can be used not only to model disease
foci expansion but also to examine effects of development of multiple foci on
epidemics (Xu and Ridout, 1996, 1998, 2000, 2001; Diggle
et al.
, 2002; Fink and