Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
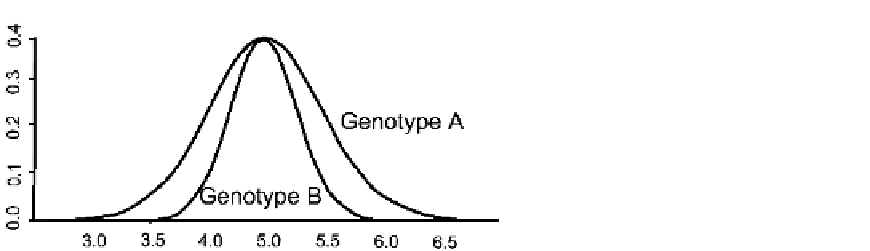
FIGURE 12.5
Canalization shown as a
reduction in variance from that exhibited by
Genotype A to that exhibited by Genotype B.
is that canalization evolves by stabilizing selection, which not only removes deviants from
the population but also favors mechanisms that suppress the expression of variation
(
Waddington, 1942; Schmalhausen, 1949
). As
Schmalhausen (1949)
put it, stabilizing selec-
tion produces a stable form by creating a regulating apparatus. Canalization, according to
this hypothesis, is the long-term effect of stabilizing selection. If we look at the distribution
of a phenotype, canalization is evident by a reduction in variance; compared to Genotype
A, Genotype B is more canalized (
Figure 12.5
).
Canalization is now often subdivided into genetic and environmental canalization
according to the source of the variation that is buffered. Canalization of genetic variation,
including novel mutations, is termed “genetic canalization” (
Kawecki, 2000; Elena and
Lenski, 2001; de Visser et al., 2003
), whereas canalization of environmental variation is
termed “environmental canalization” (for recent reviews of these concepts, see
Debat
and David, 2001; Hallgr
´
msson et al., 2002; Willmore et al., 2007
). That genetic and envi-
ronmental canalization are distinguished in this classification scheme does not imply
that the two forms of canalization are physiologically distinct. A still open question is
whether they are. Answering that question is complicated by the several distinct forms
of environmental canalization, which is now subdivided into the canalization of varia-
tion
across
environments (“macroenvironmental canalization”), and canalization within
environments (“microenvironmental canalization”). Macroenvironmental canalization is
the converse of phenotypic plasticity. One rationale for distinguishing macro- from
microenvironmental canalization is that plasticity need not reduce the ability to buffer
randomvariationwithinanenvironment.Evenasteepnormofreactionmightbewell
canalized.
Because macroenvironmental canalization is the converse of plasticity, macroenviron-
mental canalization is studied using the methods introduced in the previous section.
Microenvironmental canalization is usually studied by comparing variances. In studies of
shape, a variance can be calculated by measuring the Procrustes distance of each individ-
ual from the mean:
P
j
5
1
D
j
ð
Var
(12.2)
5
N
1
Þ
2