Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
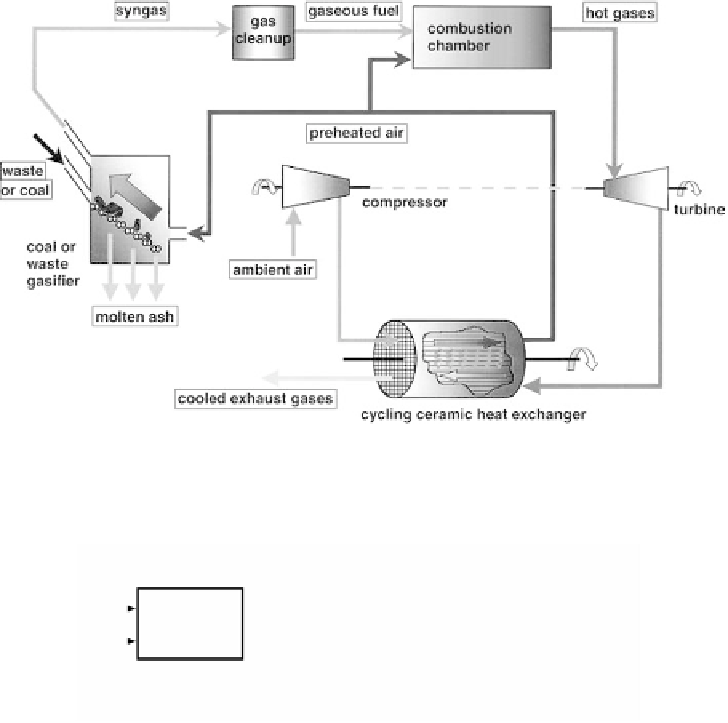
FIGURE 6.5
A schematic diagram of high temperature w
aste gasification and industrial gas
turbine system.
Product
Raw
Material
Steam
Waste
Syngas
Boiler or
Power
Generator
Gasification
of Waste
Production
Facility
Energy
Electricity
High
Temp. Air
High Temp.
Slag (Useful for road
bed construction)
FIGURE 6.6
Prospects for future ultra-lo
w waste generation from a production facility.
P
art of the energy in the syngas may be used for high temperature air/steam pre-
heating and the remainder may be used for power generation, steam generation, and
industrial heating. With a proper design various undesirable constituents in the waste
can be recovered, such as heavy metals (Fe, Cu, Al), inorganic compounds in the
form of nonleachable slag, and sulfur and chlorine.
The proof of concept for the
overall process shown in
Figure 6.7
requires validation. The main features of this
waste-to-energy conversion are as follows:
5
1. Conversion of solid wastes and low grade fuels (including coals and high-
moisture-containing municipal and industrial wastes) to clean gaseous fuels
having low to medium calorific value. The composition of the gaseous fuel
can be adjusted via some control of the chemistry, e.g., gasification, pyrol-
ysis, or reforming of the waste with steam and high temperature air, thus
increasing the calorific value of the gases produced.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search