Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Company
A
B
C
Actual fuel consumption, Mcal/ton
250-25
9
22
5
24
2
Calculated results, Mcal/ton
259
22
4
23
8
32000
30000
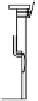
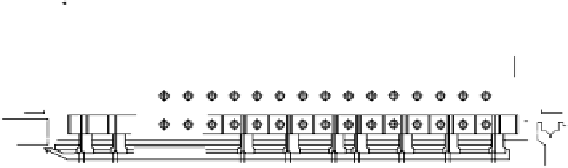
FIGURE 5.40
High performance reheating furnace for slabs of 285 ton/h (unit = mm).
40000
38000
FIGURE 5.41
Conventional reheating furnace for slabs of 285 ton/h (unit = mm).
heat recovery rate is at its maximum for each heating value.
Figure 5.49
is a graph
obtained by choosing the specific point in
Figure 5.48
of the furnace length =
30 m.
The tendency for the fuel consumption to increase with a decrease of the calorific
value is also seen with the ratio of exhaust gas volume/air shown in
Figure 5.47
.
This is caused by the difference in exhaust gas volume.
The air ratio also has a large effect on the fuel consumption. The effect was
studied on a reheating furnace for slabs of 250 ton/h. Five factors were studied in
combination, and the results of these studies are shown in
Figure 5.50
.
These factors
are the effect of air ratio, furnace length, heat-recovery rates, charging and discharg-
ing temperatures, processing capacity, ton/h, and the slab thickness.
























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search