Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Heat transfer inside the steel is calculated using a non-steady finite-difference
method (temperature-converted temperature-retained heat method) shown in
Figure
5.33
by “Heat transfer testing and its calculation method for a continuous reheating
furnace” edited by the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan. Concerning the thermal
properties of semifinished steel, the retained heat and the conversion temperature of
steel are applicable to the 22 types of steel addressed in “Heat transfer testing and
its calculation method for a continuous reheating furnace.” The following sections
are examples of average specific heat and thermal conductivity
(
Figures 5.34
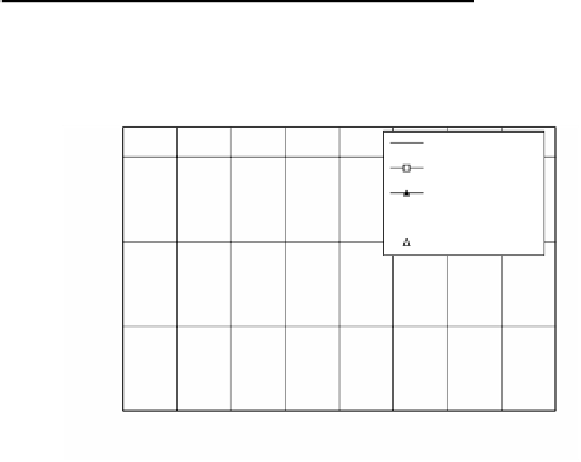
In the case of the one-dimensional heat transfer partial
differential equation, the finite-difference method of:
cross point of calculation
Interval
∆
x
is used, which is obtained by linear differentiating:
by retained heat to conversion temperature method.
FIGURE 5.33
One-dimensional calculation method of heat conduction in steel.
Rimmed steel
Killed steel
Low carbon steel
3.5% Ni steel
18-8 stainless steel
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
Temperature,
°
C
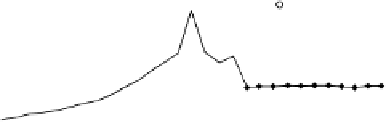
FIGURE 5.34
Examples of the relationship between steel temperature and average specific
heat.






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search