Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
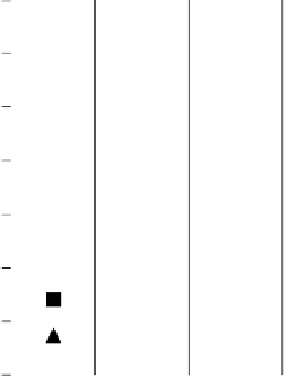
0.14
Srivatsa
0.12
One step
0.10
Jones
0.08
0.06
0.04
0.02
0.0
21.0
15.9
10.5
5.0
O volume fraction in air flow, %
2
FIGURE 3.7
Comparison of lifted height of flames.
3.2.5.3 Influence of Jet Velocity on Flame Lift Height
In the numerical simulations, the rim thickness of the fuel nozzle was assumed to
be zero, which is different from the real experimental equipment. So, the fluid
dynamic influence of the burner rim on the flame stability is somewhat different
from the actual condition, and the transition from laminar to turbulent in relation to
the increase in fuel ejection velocity cannot be seen exactly by use of
k-
ε model.
However, the influence of reaction model can be compared and discussed, undis-
turbed by other factors.
Figure 3.9
s
hows the flame lifted height in terms of ejection
velocity of fuel flow. Since the definition of the flame lifted height used here is the
distance from the nozzle tip to the point where the H
2
O concentration is 0.4%, as
stated above, the fuel flow rate inevitably affects the results. However, if the different
definition 0.02% of H
2
concentration is used, the lifted height and its v
ariation show
considerably different results.
It should be noted that the lifted height in experiments would be defined by the
visible or detectable intensity of optical emissions, which must be related to a certain
amount of apparition of intermediate species. It would be ideal if a quantity reflecting
the visually observed lifted height were used for the definition of lifted height in
simulations. But, as visually observed flame emission is mainly related to the lumi-
nescence of radicals in the flame, it is difficult to predict the intensity of emission
using simplified reaction mechanisms alone.
Regarding the desirable characteristics of combustion model to be used in the
numerical simulation of HiTAC, Srivatsa's model has shown better features among
the three. However, study of the empirical constants relevant to the proposed mech-
anism is still in progress. At present the following conclusions regarding the com-
bustion model for HiTAC have been reached:









Search WWH ::

Custom Search