Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
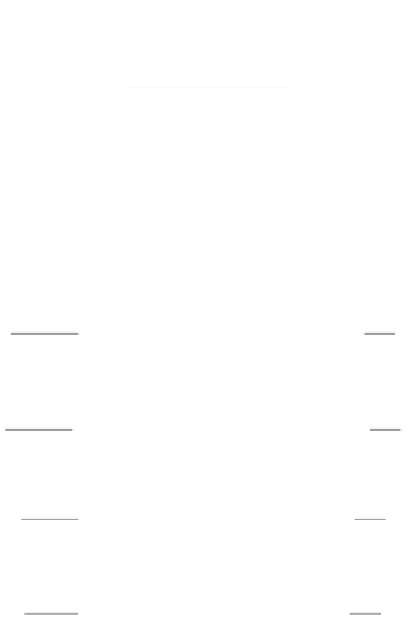
Reaction Rate Constants for Jones's Reaction Mechanism
Reaction Rate Formula
A
d
a
b
E
cal/mol
3.8
0.30 × 10
9
0
1.0
0
1.00
30,000
3.9
0.44 × 10
12
0
0.5
0
1.25
30,000
3.10
0.68 × 10
16
-1
0.2
5
1.50
40,000
3.11
0.275 × 10
10
0
1.0
0
1.00
20,000
1
2
O
CO
+
O
(R1)
2
2
1
2
OHO
H
+
(R2)
2
2
2
No reverse reactions are considered in these reactions. It is likely, therefore, that
the forward reactions advance beyond chemical equilibrium in combustion inside a
furnace with a long residence time. The reaction rate is given for each of the four
reactions as follows:
[
]
=−
d
CH
E
RT
[
] [
a
]
[
b
]
c
4
x
10
CH
O
CH
exp
(3.12)
4
2
3
dt
[
]
=−
d
CH
E
RT
[
]
[][ ]
a
b
c
3
x
10
S
CH
O
CH
exp
(3.13)
3
2
4
dt
[
]
=−
d
CO
E
RT
]
[][ ]
b
c
[
a
x
10
CO
O
H O
exp
(3.14)
2
2
dt
[]
=−
d
H
E
RT
[][]
[
a
b
]
c
2
x
10
HO
H
exp
(3.15)
2
2
3
dt
where [ ] indicates mol concentration [mol/cm
3
],
S
= 7.93 exp(-2.48φ ), and φ is the
initial global equivalence ratio, whose value cannot be unity or larger. Values of the






Search WWH ::

Custom Search