Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1373
1323
1273
1223
1173
1123
1073
1023
973
10
8
5
3
Oxygen contents of air, %
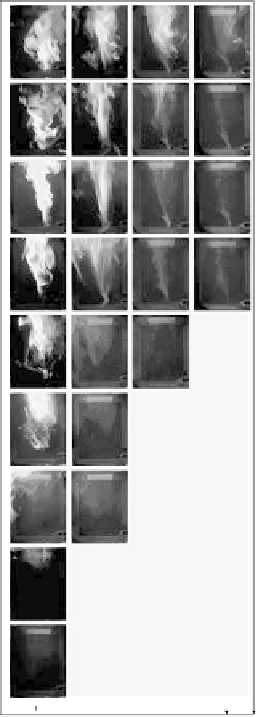
FIGURE 2.81
Spray flame at 0.3 MPa of the spray pressure in the high temperature preheated
diluted air.
2.4.1.4 Discussions
2.4.1.4.1 Blowout of Flame
A flame burning at a small distance from the exit of a nozzle, that is, a lifted flame,
was formed and blew out as the in-furnace temperature decreased. It can be consid-
ered that the reason for the flame blowout is that, as the in-furnace temperature
decreases, the fuel droplets form a steam layer, which prevents the fuel droplets
from gaining enough energy to cause autoignition.
Furthermore, the blowout of the flame occurred at a higher temperature, with
higher air dilution rate. However, the curves shown in
Figure 2.77
as a result of the
experiment may change depending on the flame to be formed and the structure of
the combustion device. If the autoignition temperature as a specific characteristic of
























Search WWH ::

Custom Search