Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
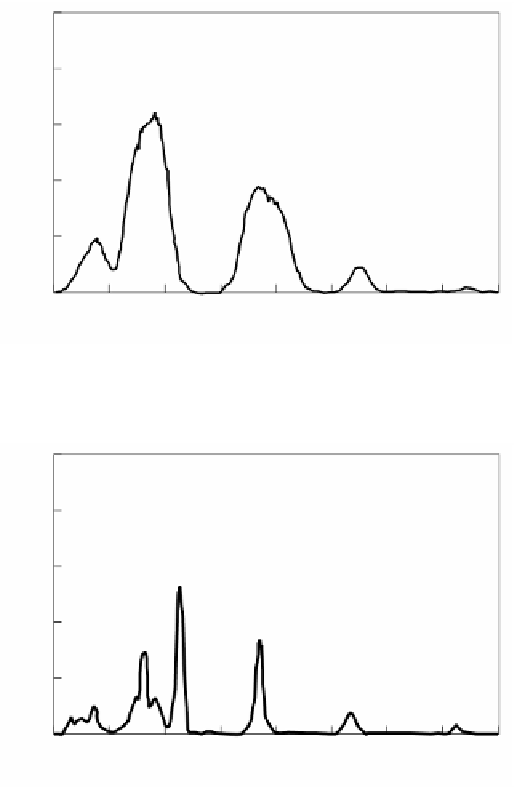
100
H O 5%
N 95%
2
2
Incident from nongray gas layer
80
60
40
20
0
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
cm
-1
Wavelength,
ν
100
Incident from nongray gas layer
H O 19%
CO 9.5%
N 71.5%
2
80
2
2
60
40
20
0
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
cm
-1
Wavelength,
ν
FIGURE 2.73
Wavelength characteristics of CO
2
/H
2
O mixed gas.
never uniform but change inevitably near furnace walls or the objects to be heated,
and for this reason there are many problems in analyses that neglect this fact.
Further, because a study of radiation heat transfer effects cannot be applied for
actual purposes unless it is done in a three-dimensional condition, conventional
analytical techniques are not adequate. For this reason, with a three-dimensional
radiation, analysis of nongray gas has to be in the form of a numerical solution.
When studying the radiation effect of nongray gas, the value of monochromatic
absorption coefficient has to be calculated. Introducing the Elsasser model and using
wave number á 1/m, the coefficient is expressed as below:



Search WWH ::

Custom Search