Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.2
0.9
H
2
CCCH/2
C
5
H
5
C
6
H
5
10
C
10
H
7
S
10
2
0.6
0.3
C
7
H
7
C
5
H
5
L 10
3
0
8
0
2
4
6
Time, s
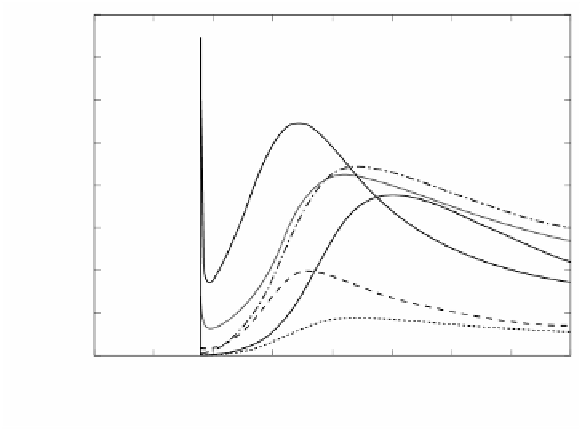
FIGURE 2.66
Temporal profiles of some important radicals in the first 8 s of PAH formation
mechanism at φ = 5.
2.0
INDENE
C
6
H
6
/3
1.6
A2R5
C
10
H
8
1.2
PYRENE
0.8
CPCDPYR
BGHIF
0.4
0
0
5
10
15
20
Time, s
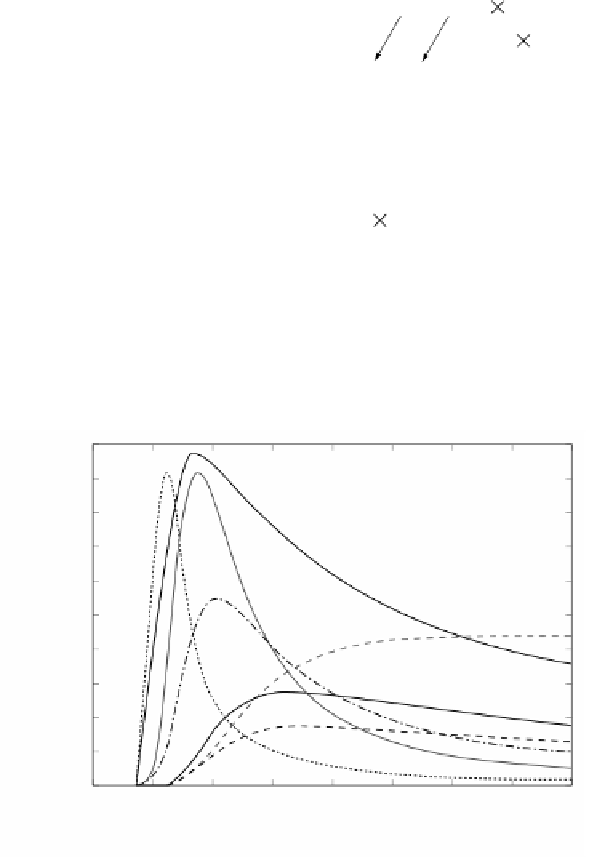
FIGURE 2.67
Temporal profiles of the most abundant species at φ = 5 up to 20 s.
proceeded in the reverse direction H
2
CCCH → C
3
H
4
P, now proceeds in the forward
direction, producing H
2
CCCH. In addition, R532 also forms H
2
CCCH, from C
3
H
4
;
the rate of this reaction in the second stage is about 1/3 of that at the first stage, but
it lasts now for more than 3 s. H
2
CCCH combines then with either C
2
H
2
(R431) to
form C
5
H
5
(L), or C
3
H
4
(R388) to form C
6
H
6
(benzene). The linear C
5
H
5
L becomes



Search WWH ::

Custom Search