Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
not require much, if any, fertilizer. Despite low maintenance require-
ments, Bahia grass must be mowed on a regular schedule, otherwise it
produces tall and quite unsightly seed-heads. Unlike
P. vaginatum
, Bahia
grass does not perform well in high-pH soils and does not have good
tolerance to shade, traffic or salinity. Bahia grass has an open growth
habit; that is, its stems grow more vertically than horizontally and often
permit easier encroachment by weeds into open-space areas. Like
P. vaginatum
, Bahia grass has quite a low tolerance for many herbicides,
making chemical weed control difficult.
The genus Axonopus (Panicoideae)
Axonopus affinis
Chase, known as carpet grass, and
Axonopus compressus
(Sw.) Beauv., known as tropical carpet grass, are coarse-textured, low-
growing, light-green turf-grasses that spread by stolons (Fig. 2.8). Both
species can be established from seeds or vegetative propagation. They are
used mainly in low-quality turfs, along roadsides, on slopes, etc. Carpet
grass tolerates low fertility and very acidic soils, requires little mainten-
ance, and when established, holds on to soil on highly eroded slopes. Its
importance is increasing especially in coastal areas with sandy soil.
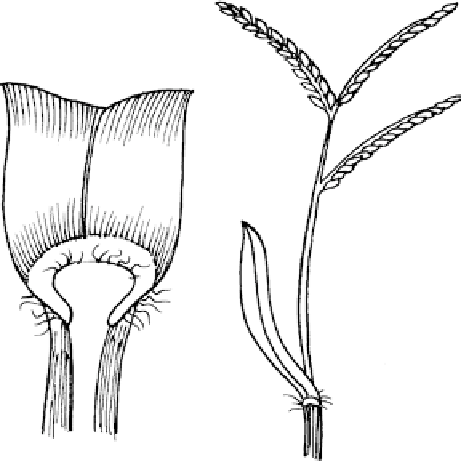
Fig. 2.8. Carpet grass (Axonopus affinis). Leaves folded; ligule a fringe of hairs fused
at the base; collar narrow, continuous, sometimes with hairs; auricles absent; blades
short, 4-8 mm wide, with short hairs near tips; seed-head three spikes; spikelets
widely spaced in two rows. (Drawing by R. Castro.)