Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
80
70
60
50
40
30
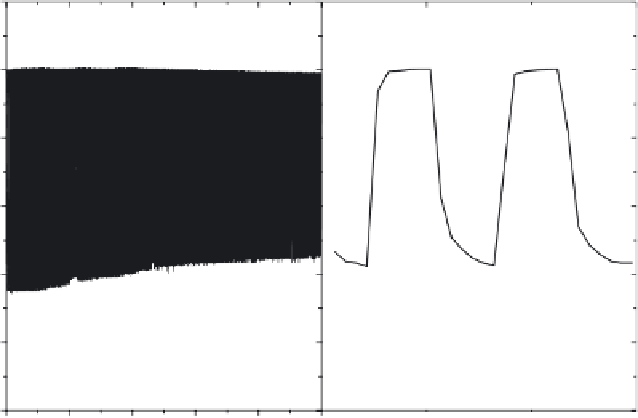
After 750 cycles
Bleaching time 40 s
Colouring time 120 s
1400 cycles
20
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
Time (s) × 10
6
11.5
Initial data on transmittance modulation of luminous radiation in
an electrochromic foil device made by roll-to-roll manufacturing and
continuous lamination.
more than 50 years (Morin, 1959). However, vanadium dioxide is not
directly applicable to glazings, and three particular challenges can be identi-
fi ed as elaborated in Section 11.3.1 below. In particular, the modulation of
the solar energy throughput must be suffi ciently large in order to have a
signifi cant impact on the buildings' energy expenditure, and this leads to
the recently introduced concept of 'nanothermochromics' (Li
et al.
, 2010),
which also is advantageous for yielding a large luminous transmittance as
discussed in Section 11.3.2. The luminous transmittance can be further
enhanced by doping of the VO
2
, especially by magnesium, as discussed in
Section 11.3.3. Finally, the modulation of the solar energy throughput must
occur in the vicinity of a comfort temperature of about 25°C, which again
can be accomplished by doping - in this case most expediently by tungsten
- as elaborated in Section 11.3.4.
11.3.1 Vanadium dioxide-based thin fi lms: three challenges
Vanadium dioxide is an interesting and complex material with at least seven
different polymorphs among which rutile VO
2
(R), monoclinic VO
2
(M)
(Morin, 1959), and triclinic VO
2
(T) (Mitsuishi, 1967) phases are similar
in structure, and there are also tetragonal VO
2
(A) (Oka
et al.
, 1990),
Search WWH ::

Custom Search