Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
nanocomposite include the type of clay, the choice of clay pre-treatment,
the selection of polymer component and the way in which the polymer is
incorporated into the nanocomposites (Pinnavaia and Beall, 2000).
Common clays are naturally occurring minerals and are thus subject to
natural variation in their constitution. The purity of the clay can affect fi nal
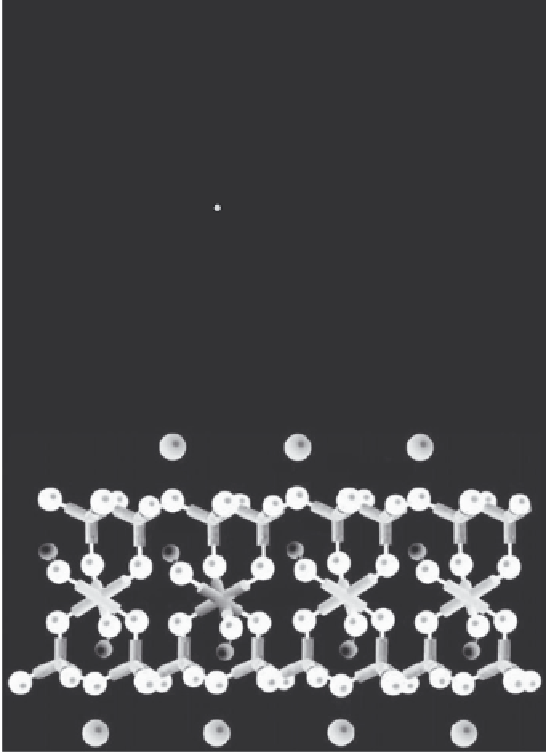
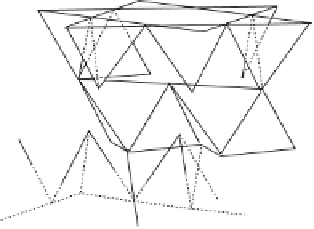
nanocomposite properties. Many types of clay are alumina-silicates, which
have a sheet-like (layered) structure, and consist of silica SiO
4
tetrahedron
bonded to alumina AlO
6
octahedron in a variety of ways. A 2 : 1 ratio of the
tetrahedron to the octahedron results in mineral clays, the most common
of which is montmorillonite (Fig 6.1). The thickness of the montmorillonite
layers (platelets) is 1 nm and aspect ratios are high, typically 100-1500
(Grim, 1959). The degree of expansion of montmorillonite is determined
6O
4Si
O
4O +2(OH)
2Al
4O +2(OH)
d
4Si
6O
Cation
Si, Al
OH
Al, Mg
O
O
Cation
Si
OH
O
Al
6.1
Structure of montmorillonite.




































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search