Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
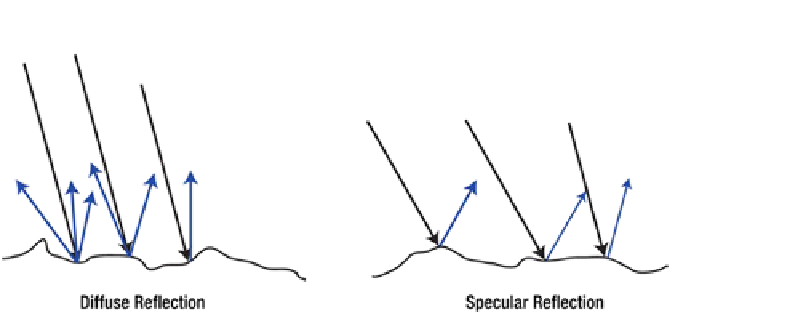
Figure 11-2.
Diffuse and specular reflection
Specular reflection will manifest itself as highlights on objects. Whether an object will cast
specular reflections depends on its material. Objects with rough or uneven surfaces, like skin or
fabric, are unlikely to have specular highlights. Objects that have a smooth surface, like glass
or a marble, do exhibit these lighting artifacts. Of course, glass or marble surfaces aren't really
smooth in an absolute sense, either. Relative to materials like wood or human skin, though, they
are very smooth.
When light hits a surface, its reflection also changes color depending on the chemical
constitution of the object it hits. The objects we see as red, for example, are those that reflect
only the red portions of light. The object “swallows�? all other wavelengths. A black object is one
that swallows almost all of the light that is shone on it.
OpenGL ES allows us to simulate this real-world behavior by specifying light sources and
materials of objects.
Light Sources
We are surrounded by all kinds of light sources. The sun constantly throws photons at us. Our
monitors emit light, surrounding us with that nice blue glow at night. Light bulbs and headlights
keep us from bumping or driving into things in the dark. OpenGL ES enables us to create four
types of light sources:
�?�
Ambient light
: Ambient light is not a light source per se but rather the result
of photons coming from other light sources and bouncing around in our
world. The combination of all of these stray photons makes for a certain
default level of illumination that is directionless and illuminates all objects
equally.
�?�
Point lights
: These have a position in space and emit light in all directions.
A light bulb is a point light, for example.
�?�
Directional lights
: These are expressed as directions in OpenGL ES and are
assumed to be infinitely far away. The sun can be idealized as a directional
light source. We can assume that the light rays coming from the sun all hit
the earth at the same angle because of the distance between the earth and
the sun.