Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
400
200
100
6
80
40
20
10
Acenaphthene
9-Methylacridine
4
Phenanthene
Dibenzothiophene
Benzene
2
1
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
c
eq
/mg L
-1
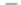
FIGURE 11.5
Adsorption isotherms for acenaphthene, 9-methylacridine, phenanthrene, and dibenzo-
thiophene and for benzene (for comparison) on the activated carbon Epibon Y12×40 (sieved
63-125 μm) in deionized water at
T
± σ = 20 ± 3°C. Curves are from the results of the Langmuir-
Freundlich model. Data in parenthesis are defined as outliers and not used. Linear regression
for benzene represents the Freundlich model.
250
1.0
2-Methylquinoline
c
0
= 11-24 mg/L
Exp. load (calculated using
Freundlich model)
0.8
200
Fit exp. load
Calculated load of
mixture (IAS, Freundlich)
0.6
Fraction neutral molecule
in solution (pK
a
= 5.86)
150
0.4
100
0.2
50
0.0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
pH
FIGURE 11.6
The adsorption loads of 2-methylquinoline on AC Epibon Y12×40 evaluated from pH-
dependent Freundlich isotherms (
T
= 20°C). In addition, loads calculated with the IAS-model
and the neutral fraction present in the solution are shown.









































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search