Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
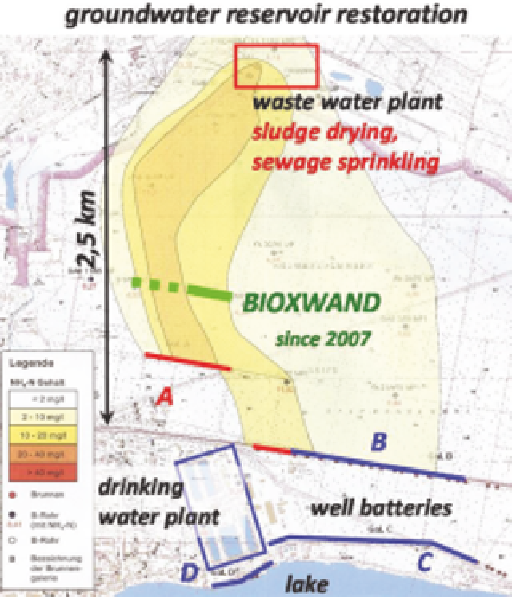
FIGURE 10.12
Site map of the BIOXWAND application area.
local variations in the injection regime based on hydrogeological profiling,
monitoring was used to achieve a full-section PRB effect. The oxygen con-
tent of the injection gas varied between 20% (e.g., same as the atmosphere)
and 100%. Gas injection cycles of 1-2 h were followed by breaks of 3-5 h,
and coherent gas flow velocities >1 m/h were detected next to the injection
lances. Vertical gas escape into the unsaturated soil zone was monitored as
it occurred (e.g., when it exceeded the local aquifer gas storage and retarda-
tion capacities). In this case, stripping did not occur due to a lack of volatile
solutes in the groundwater.
The BIOXWAND performance showed that it was impractical to aim
for a quick remediation (e.g., satisfying the entire oxygen demand of
64 tonnes per 100 m) during the first year of barrier operation. This can
lead to decreased operating efficiency with high gas losses mainly due to
heterogeneous gas distribution, diffusion-limited gas dissolution, the vari-
able and developing kinetics of matrix to groundwater exchange, and bio-
chemical transformation processes. In the case of BIOXWAND, an initial
3-year operating regime was conducted, during which a total oxygen mass
Search WWH ::

Custom Search