Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
An RGBZ monitoring system is comprised of a combination of five ele-
ments. These are groundwater observation and sampling points or wells, an
in situ sensing array for detection of the dissolved gas distribution domain,
a detector set for estimation of pneumatic and hydraulic gas propagation, a
measurement system to quantify dynamics of gas saturation in the gas stor-
age zones, and finally, a soil gas composition control system.
Techniques that can be used to efficiently control the performance of a gas
PRB and optimize the impact to in situ transformation processes are available
as an integral mass balancing method for injection gases, and as an algorithm
for performance optimization. Modeling techniques can be used for the plan-
ning and evaluation of gas PRB applications. Due to their reactive multiphase
multicomponent nature, they are normally too complex and the uncertainty
is too high, rendering them of questionable value as a decision making tool.
10.3.2 Gas Injection Devices
10.3.2.1 Gas Lances
Lances can be installed by drilling and sounding or direct push methods
(Figure 10.6). A number of technical requirements must be met: (1) prevention
of ground loosening during installation; (2) high-precision depth-oriented
positioning of filter elements to 50 m below the surface, including in heavy
ground penetration conditions; (3) a gas-tight vertical sealing of the injection
VIL
RIL-Ty pe B,
DIL-Ty pe A
BIL
RIL-Ty pe A
DIL-Ty pe B
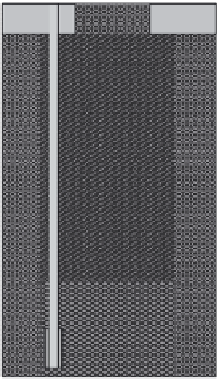
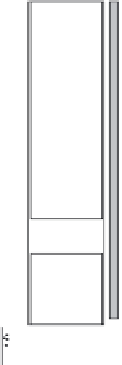
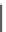
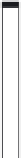
FIGURE 10.6
Variants of injection lance installations for DGI applications. BIL—drilling; RIL—percussion
sounding; DIL—CPT-based penetration sounding; and VIL—vibration sounding.














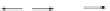







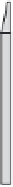













































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search