Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
Gas injection
Injection lance
Gas-PRB
Upstream
Downstream
Aerobic
transport zone
Anaerobic
transport zone
Gas propagation
and dissolution
(b)
Supply with reactants
removal of reaction products
Gas injection
Gas injection
Surface
Reactor
Pump
In situ
sediment reactor
for conditioning
i.e., iron removal
In situ
sediment reactor
for posttreatment
i.e., oxygen wall
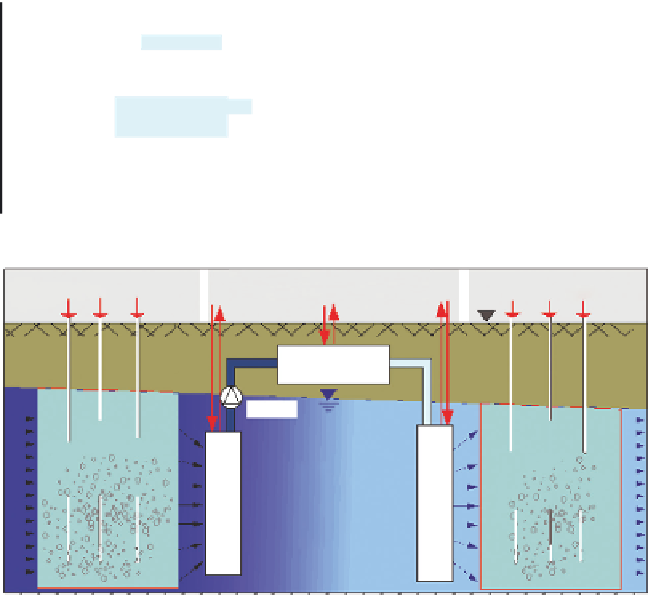
FIGURE 10.1
Technology application variants for RGBZ. (a) Stand-alone full-section gas PRB with sequential
reactive zones (patent EP 1550519 “BIOXWAND”). (b) Pre/postreactive gas zones of a drain
and gate treatment train for complex groundwater and subsurface decontamination (patent
DE 10310986 “GFIadags”).
The methods of RGBZ operation used in this research are direct gas injec-
tion (DGI) and application options for low-pressure (NDI) and high-pressure
injections (HDI), which are discussed. It is noted that the term “sparging” is
not used for RGBZ applications, as it is linked to applications that generate a
gas which escapes from the groundwater zone and strips groundwater con-
taminants. Biodegradation is only an additional effect of sparging; a soil gas
extraction and treatment system is needed.
The RGBZ technology has been approved by German Environmental
authorities (ITVA, 2010) and additional applications in regard to enhanced
natural attenuation (ENA) are anticipated.









































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search