Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
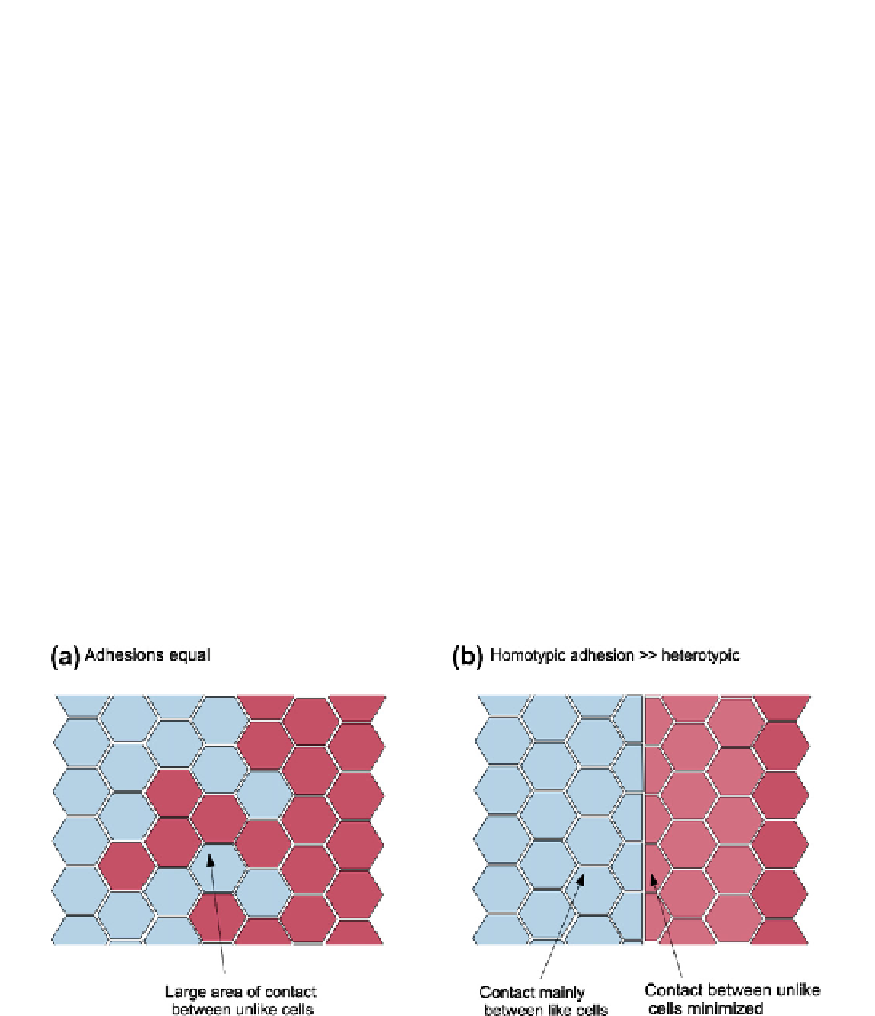
two adhesion molecules bind and adhere, they reduce overall free energy (this change in
energy is what makes them 'want' to adhere). The overall energy of a mixture of the two
cell types will therefore be at a minimum when as many adhesion molecules as possible
face their own kind on an identical neighbour cell and as few as possible face the other
cell type. This condition would be best fulfilled where cells of the two types arrange them-
selves to minimize the length of their border (
Figure 21.3
). Under these conditions, any cells
that tried to invade the other territory would reduce the fraction of their surface that faces
strongly adhesive neighbours and would increase the fraction of their surface area that faces
cells with the wrong kind of adhesion molecule. Invasive behaviour would therefore be
resisted.
This model for boundary formation and maintenance is one of the oldest, and appears to
be supported by the existence of compartments that do indeed express different cell-cell
adhesion molecules. An example is again provided by the early central nervous system,
in this case by the endbrain (telencephalon), which consists of five distinct regions: the olfac-
tory bulb, the neocortex, the archaeocortex, the basal ganglia and the septum. Each
expresses its own characteristic set of molecules. Cells of the neocortical neurepithelium,
for example, express the homophilic, calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecule cad-
herin 4, while those of the adjacent basal ganglion compartment express its close relative,
cadherin 6.
ref13
If cells from the neocortex and from the basal ganglia zones are isolated
from 14-day-old rat embryos, dissociated into single cell suspensions and mixed, they or-
ganize themselves into two distinct zones with a fairly straight boundary.
14
This sorting
is required on calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion moelcules, and could be eliminated
FIGURE 21.3
Boundary maintenance according to the theory of adhesive differences. In both parts of the
diagram, cells of one compartment are coloured blue and the cells of the other are coloured pink. In (a), cells express
the same adhesion molecules so mixing carries no energetic cost. In (b), they express different adhesion molecules
so that each cell adheres best to its own kind. Since adhesion minimizes free energy, thermodynamics leads the cells
to minimize the total area of contact with a less adhesive cell type, and this results in the border being short and
invasion being resisted.