Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
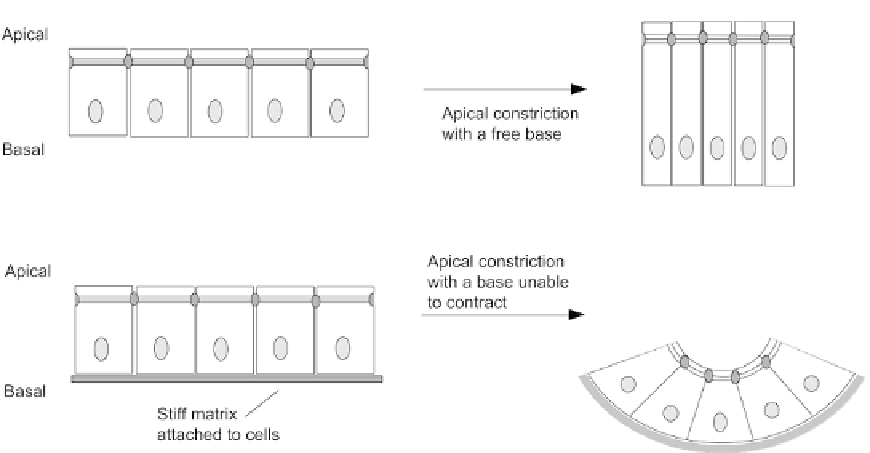
FIGURE 18.8
The importance of basal restraint to involution driven by apical constriction. With the basal
surface free to change diameter, apical constriction could just result in the production of tall, columnar cells,
especially if neighbouring structures (not shown) showed significant resistance to the deformation that the invo-
lution of the depicted cells would force on them. Where the basal surface of the cells is attached firmly to an
underlying matrix that resists compression, the basal surface will not be able to contract, and invagination has to
result.
ORTHOGONAL INVAGINATION: NEURAL TUBE
FORMATION IN VERTEBRATES
The neural tube of vertebrates, which forms the brain, spinal cord and neural crest, derives
from an area of the dorsal ectoderm epithelium called the 'neural plate'. The events that
shape it first into a trough, by orthogonal invagination, and then a neural tube (
Figure 18.9
),
are broadly similar in all vertebrate classes although there are inevitable differences in detail
caused by different embryonic geometries.
The first event of neural tube formation is an apicobasal thickening of the epithelium,
similar in character to that seen with the lens placode. In birds, at least, this thickening will
take place even when the presumptive neural plate is isolated from its surrounding tissues,
so it must rely on strictly local mechanisms.
17
The apico- basal elongation of neural plate cells
is associated with the presence of arrays of microtubules extending from base to apex of the
cell and it can be inhibited by microtubule-depolymerizing agents.
18
e
21
It may therefore, in
this case, be derived by internal tubule-generated forces (Chapter 5), although, as most micro-
tubule-depolymerizing agents would be expected to inhibit mitosis, an effect via inhibition of
proliferation cannot be ruled out.
The next event is the formation of curvature in the neural plate, a process sometimes
referred to as 'kinking'.
22
This curving is localized to specific 'hinge points' and generates
convex or concave curvature depending on where it takes place. At the edges of the neural