Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
In general, the structure of an epithelium sketched above is maintained during morpho-
genesis so that it remains tightly sealed. This means that many of the morphogenetic
processes used by mesenchyme cells, such as migration and condensation, are unavailable.
Instead, morphogenesis has to take place by growth, folding and invagination of the sheet.
These distortions usually require cells to stream past each other altering their neighbour
relationships, and this in turn requires that the junctions between epithelial cells and
between cells and the matrix are labile and can be released when required. This release
cannot be global
d
that would destroy the epithelium
)
d
but must be restricted to only
the junctions that have to move. The pattern of junction modification is discussed further
in Chapter 16. The molecular mechanisms that control it are not yet understood although
internal regulators of cell-cell adhesion, such as the small GTPase Rap1, have been
identified.
26
THE MAKING OF AN EPITHELIUM
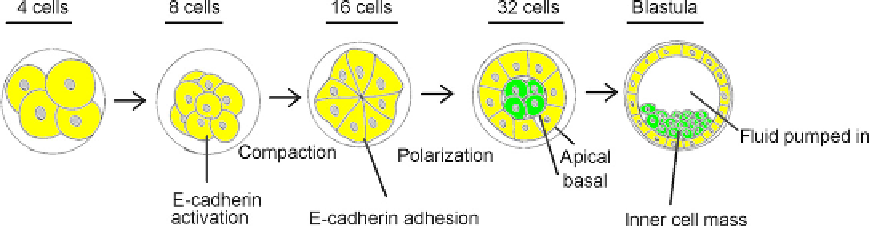
Most new epithelia arise from the morphogenesis of an existing epithelium but the forma-
tion of the very first epithelium of the embryo, that of the blastula, has to be an exception. In
the mouse, the development of the first epithelium begins when the embryo contains a mere
eight cells (
Figure 15.4
). At this time, E-cadherin already present in the embryo is phosphor-
ylated and becomes functional.
27
As it reaches the cell membranes of the blastomeres that
produce it, their mutual adhesion increases and they maximize their contact. This adhesion,
and the compaction of the embryo that results, is inhibited by function-blocking anti-
E-cadherin.
27
Between the 8- and 32-cell stages, other junction components are transcribed in
a sequence. For example, gap junctions components are made at the 8-cell stage,
28
the tight
junction protein ZO1
- is transcribed from the 8-cell stage, starting about an hour after
E-cadherin-mediated compaction, cingulin is made at the 16-cell stage but ZO1
a
a
þ
is not
FIGURE 15.4
Formation of the first epithelium of a mouse.
)
Some examples of morphogenesis do involve complete breakdown of the epithelium (for example, during
the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions required to supply mesenchyme cells to the developing heart)
25
but these are not being discussed here.