Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
reduces the ability of cdc42 to activate WASP and thence Arp2/3-mediated polymerization of
protrusive actin filaments. Slit therefore directly antagonizes the main pathway that encour-
ages leading edge advance, which presumably explains why it antagonizes migration. What
is not yet clear, though, is how shallow external gradients of Slit can steer migratory cells as
well as just slowing them down. Perhaps there are further internal feedback systems to turn
small differences in external concentration into strong internal gradients of second messen-
gers, or perhaps the activity of Robo is itself enough to bias and reorient the feedback systems
(PI(3,4,5)P
3
/cGMP, and so on) described ealier
in this chapter
in the section on
chemoattraction.
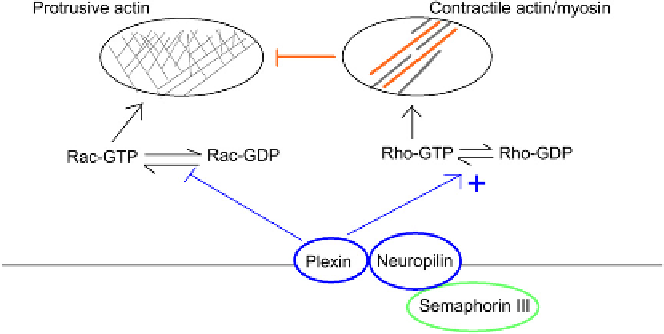
Semaphorins constitute another important family of repulsive molecules, some of which
are secreted and act as chemorepellants while others remain membrane-bound and act by
contact inhibition. Semaphorin III (synonyms: collapsin I, semaphorin D) is a secreted sema-
phorin that will repel the growth cones of sensory and sympathetic neurons in culture.
54,55
It
signals via a complex of a transmembrane protein, neuropilin,
56,57
which is expressed on
subsets of neurons and also on other cells such as regulatory T cells of the immune system,
58
and which binds semaphorin III, and a plexin protein that generates intracellular signals in
response to semaphorin III/ neuropilin binding. Plexins show GAP activity
59
and interact
directly with Rac, presumably activating its GTPase activity
60
and also perhaps competing
with GEFs for Rac binding.
61
Experiments using dominant negative Rac confirm that Rac
is needed for plexins to inhibit growth cone advance.
60
Plexins therefore act in a manner
similar to Robo, in that they antagonize the ability of Rac to organize a protrusive leading
edge. In addition to having a Rac binding domain, plexins have an additional domain that
interacts with Rho (at least, D. melanogaster plexin does, and conservation of amino acid struc-
tures suggests that those of other animals do as well). Genetic analyses, using Rho mutants,
suggest that Plexin activates Rho and, therefore, assembly of contractile actin-myosin
systems.
61
The receptor system for semaphorins therefore mounts a two-pronged attack on
the protrusive activity of a leading edge, reducing the cell's ability to make Arp2/3 nucleated
FIGURE 9.10
Plexins inhibit protrusive activity both directly via Rho, and indirectly by encouraging the
formation of contractile myosin filaments that themselves inhibit formation of a protrusive actin network.