Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(g)
(e)
(f)
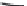
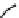
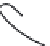
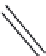
Figure 6: Several typical types of vertical-axis wind turbines: (a) Darrius;
(b) Savonius; (c) Solarwind™ [36]; (d) Helical [37]; (e) Noguchi [38];
(f) Maglev [39]; (g) Cochrane [40].
generated from a downwind turbine fl uctuates greatly. In addition, the unstable
fl ow fi eld may result in more aerodynamic losses and introduce more fatigue loads
on the turbine. Furthermore, the blades in a downwind wind turbine may produce
higher impulsive or thumping noise.
5.1.3 Wind turbine capacity
Wind turbines can be divided into a number of broad categories in view of their
rated capacities: micro, small, medium, large, and ultra-large wind turbines.
Though a restricted defi nition of micro wind turbines is not available, it is accepted
that a turbine with the rated power less than several kilowatts can be categorized

























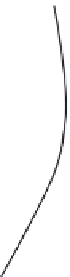















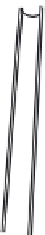



































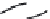











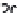


































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search