Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
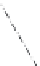
blade rotation
relative to rotor
wind
1
3
3
1
1
rotor rotation
3
2
2
2
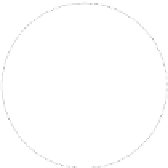
Figure 9: Principle of operation of a VAWT based on the variable pitch “Kirsten-
Boeing Propellor” concept [28].
Theoretical modelling of this type of device indicates that the maximum coeffi cient
of performance would be expected to be only
C
p,max
0.2 [29]. Like the Savonius
rotor, this rotor does have the advantage of low tip speed ratio which will likely
result in less noise and vibration issues, however, the high solidity ratio and
hence material cost means that turbines of this type are highly unlikely to be a
commercial success.
∼
2.3 VAWTs in marine current applications
One of the hot topics in renewable energy at the time of writing is the develop-
ment of marine current turbines (MCTs) to harvest the signifi cant potential of tidal
currents in various locations around the world. These devices are also known as
hydrokinetic turbines, which include those operating on the same principles but
in rivers and estuaries. Areas such as the English Channel and the north coast of
Ireland have been identifi ed as having great potential for this technology. The most
common technology currently being applied in the fi eld is that of horizontal axis
MCTs such as that developed by Marine Current Turbines Ltd. [30] and Open-
Hydro [31]. However, various research groups have investigated the feasibility
of using vertical-axis MCTs which have obvious advantages in this application,
particularly in that a yaw mechanism is not required to align the turbine with the
wind [ 32- 36 ].
3 Analysis of VAWT performance
As in the case of HAWTs, there are a number of levels of complexity with which
one might analyse the performance of the VAWTs as outlined by authors includ-
ing Touryan
et al.
[ 37 ], Strickland [ 38 ] and Wilson [ 24 ]. Allet
et al.
[ 39 ] classi-
fi ed the four main approaches to modelling of VAWTs as: (i) momentum models;
(ii) vortex models; (iii) local circulation models; and (iv) viscous models, where
the latter would include full viscous fl ow computational fl uid dynamics (CFD)













































Search WWH ::

Custom Search