Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The inverter would also include grid protection functions according to utility
standards. In the European Union this would typically be EN50438 [3], whereas
standards vary in the USA. Grid protection is primarily required to disconnect
the wind system from the grid in the event that the power produced is outside of
a frequency/voltage window (i.e. either the voltage or frequency going too high
or too low). This would suggest that a utility power outage has occurred and that
the inverter output is being fed into a “dead” line, thereby endangering utility
linemen.
An induction generator-based system would also have grid protection functions
according to EN50438. It would also have logic to connect and disconnect the
generator from the grid, usually based on generator rotation speed (rpm).
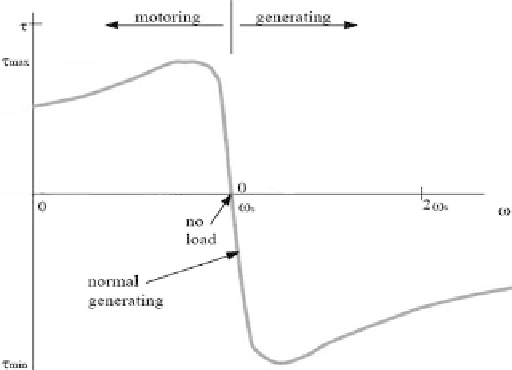
Figure 18 shows the induction machine speed
torque curve. Torque is produced
by the machine as it motors up to speed from a stopped condition. When driven
beyond the synchronous speed (
w
s
) it absorbs torque (and produces electrical
power). Normal (full load) generating torque is indicated on the curve. Therefore
the control action would allow the turbine to be driven up to synchronous speed by
the wind, and at
w
s
connect it to the grid. Similarly when the rotational speed
drops below
w
s
the machine is consuming power and so the control system discon-
nects it from the grid.
There are a number of possible variations on this approach. For example, it
could be connected on the basis of rpm as above, but disconnected on the basis of
power (i.e. when power is being consumed). Since precise connection at
w
s
is
needed (consider the torque spike that would result if connection occurred at
w
s
+
10%), rate-of-change of
w
could be integrated into the control algorithm. In some
turbines (Enertech and AOC) the machine was actually motored up to speed
(sometimes stalling airfoils have poor self-starting characteristics) when wind
speed was deemed suffi cient to generate power.
−
Figure 18: Induction machine speed
−
torque curve.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search