Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
work on wind turbines. Two distinct branches can be identifi ed: so-called free-fi eld
experiments, carried out in the open air and those performed under controlled
infl ow conditions within wind tunnels. Considerations are restricted to NASA-
AMES
blind comparison experiment
and the European MEXICO (Measurements
and Experiments in controlled conditions) project, performed in Europe's largest
wind tunnel in the Netherlands. After describing aeroelastics in Sections 5 and part 6
in general, the impact of this elaborate scientifi c work on commercial wind tur-
bines is presented. This is a somewhat diffi cult and delicate task, as most of this
work and even the results are confi dential. In practice, this means that only public-
domain work and non-standard turbines will be considered. Section 8 concludes
this discussion with a summary and an outlook for future developments after the
aerodynamics of some unconventional turbines are presented in Section 7.
2 Analytical theories
The fi rst work which provided a simple complete model of the global fl ow around
a wind turbine is the so-called actuator disk (AD) theory. It was fi rst developed by
Rankine and Froude to describe the fl ow around ship propellers. Figure 1 shows an
overview of all possible fl ow states which can occur. Recently [58] it was possible to
reproduce all fl ow states observed by Glauert from a numerical full-fi eld AD model.
The main idea is the introduction of a slipstream (Fig. 2) behind the rotor. Energy
is extracted by decelerating the infl ow
v
1
to
v
2
at the rotor and
v
3
far downstream.
Figure 1 : Flow states of propellers and wind turbines [ 12 ].


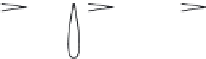


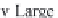



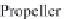

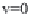






























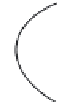




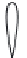

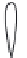






































Search WWH ::

Custom Search