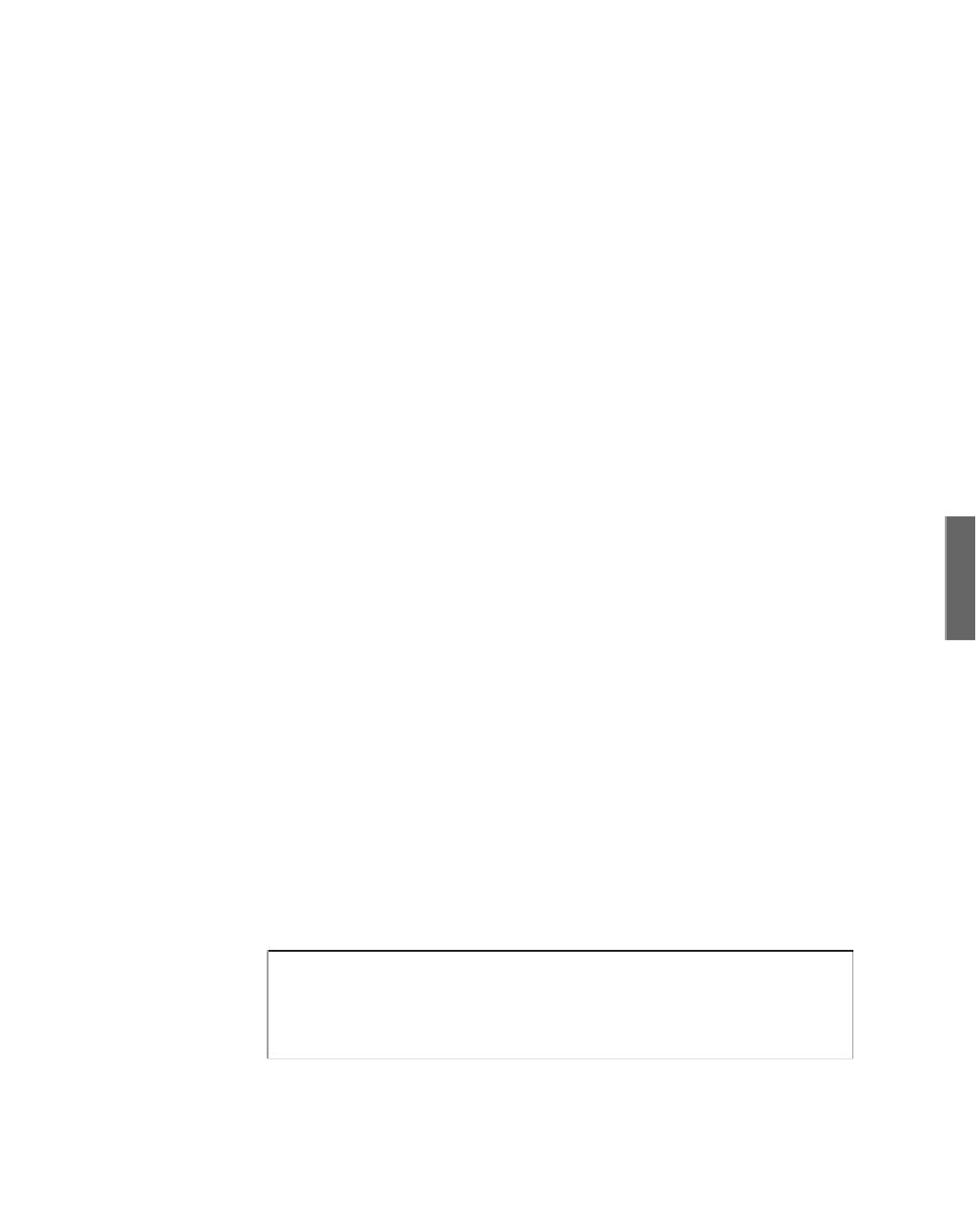Java Reference
In-Depth Information
The variable can be used only within that block. An error would result if you tried to use
the
y
variable in another part of the
testBlock()
method.
The
x
variable was created inside the method but outside the inner block, so it can be
used anywhere in the method. You can modify the value of
x
anywhere within the
method.
Block statements usually are not used alone within a method definition, as they are in the
preceding example. You use them throughout class and method definitions, as well as in
the logic and looping structures you learn about next.
A key aspect of any programming language is how it enables a program to make deci-
sions. This is handled through a special type of statement called a
conditional
.
A
conditional
is a programming statement executed only if a specific condition is met.
The most basic conditional in Java is the
if
keyword. The
if
conditional uses a Boolean
expression to decide whether a statement should be executed. If the expression produces
a
true
value, the statement is executed.
Here's a simple example that displays the message
“Not enough arguments”
on only
one condition: If the value of the
arguments.length
instance variable is less than 3
4
if (arguments.length < 3)
System.out.println(“Not enough arguments”);
If you want something else to happen when an
if
expression produces a
false
value, an
optional
else
keyword can be used. The following example uses both
if
and
else
:
int duration;
if (arguments.length < 1)
“'“server = “localhost”;
else
“”server = arguments[0];
The
if
conditional executes different statements based on the result of a single Boolean
test.
A difference between
if
conditionals in Java and those in other
languages is that Java conditionals only produce Boolean values
(
true
or
false
). In C and C++, the test can return an integer.
NOTE