Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
concentration. There were no significant dependencies of the shape constant,
n
, and the rate
constant,
k
, on the initial concentration.
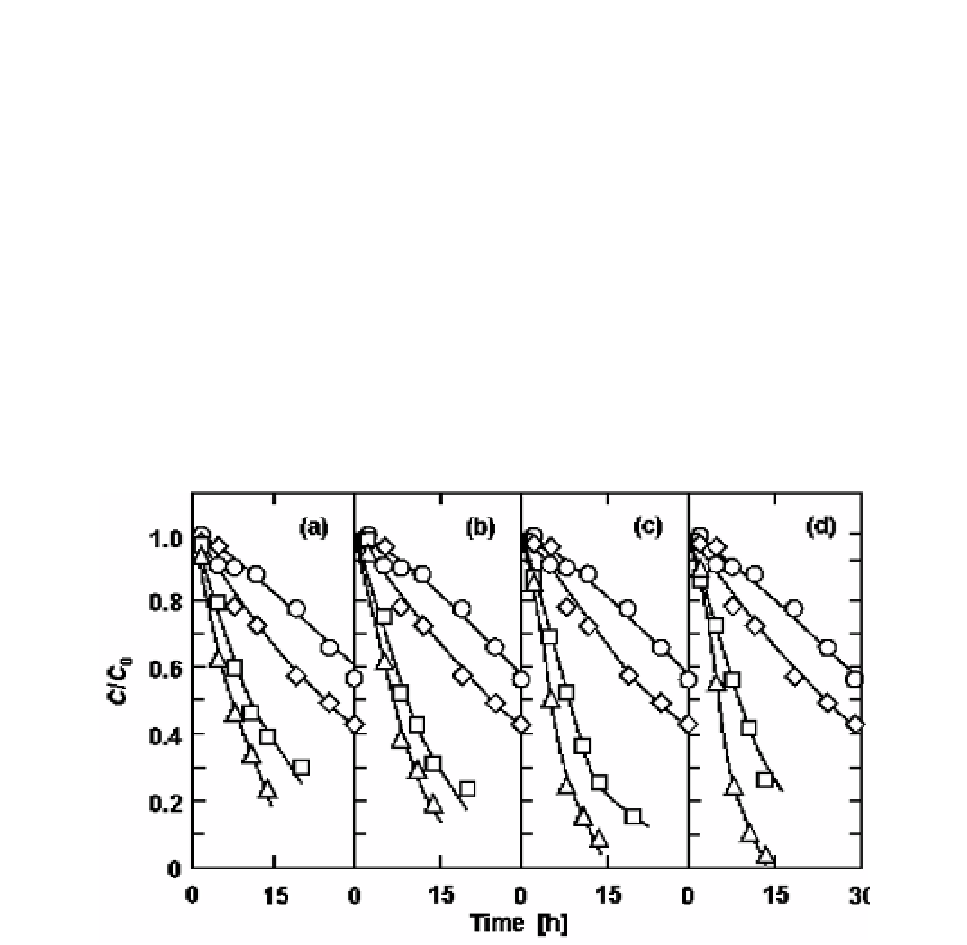
The degradation of acyl ascorbates was measured at pH 5 and different temperatures
(Figure 9). The initial concentration of each ascorbate was fixed at 2.0 x 10
-4
mol/L. The
k
value for each ascorbate is plotted versus the reciprocal of
T
in Figure 10(a). The plots for
each ascorbate lay on a straight line, and the
E
and
A
values were estimated. Both the
E
and
A
values seemed to depend on the acyl chain length of ascorbate. As mentioned above, the
hydrolysis of the ester bond did not significantly occur at pH 5, but only the oxidation of the
ascorbyl moiety of the ascorbate was responsible for the decomposition of each acyl
ascorbate. Therefore, it would be expected that the enthalpy-entropy compensation holds
during the decomposition at that pH. Equation 5 is one of the expressions describing the
compensation [49-51]:
E
=
R T
β
ln
A
+ γ
(5)
Figure 9. Decomposition of (a) hexanoyl, (b) octanoyl, (c) decanoyl and (d) lauroyl ascorbates at pH 5
and different temperatures. The temperatures were
(
{
)
30,
(
)
40,
(
)
50 and
(
U
)
60
o
C. The initial
concentration of each ascorbate was 2.0 x 10
-4
mol/L. The
C
and
C
0
represent the concentration of each
ascorbate at any time and the initial one, respectively. The solid curves were calculated using the
estimated kinetic parameters of the Weibull model.
where
T
β
is an isokinetic temperature and γ is a constant. The
E
values are plotted versus the
logarithms of the
A
values in Figure 11. The plots lay on a straight line (R
2
= 0.994). This
indicated that the decomposition of every acyl ascorbate essentially proceeded by the same
mechanism. The
T
β
value was estimated to be 39.2
o
C from the slope.
The decomposition of saturated acyl ascorbate in air was also measured at various
relative humidity and temperatures [36]. The transient changes in the fractions of the
remaining octanoyl, decanoyl, lauroyl, myristoyl and palmitoyl ascorbates at 80
o
C and at 12,
44 and 75% relative humidity. The relative humidity significantly affected the decomposition
of the acyl ascorbates. The decomposition rate of all ascorbates increased with increasing