Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 11. Reported values of the cetane number for biodiesel
Soybean Methyl
Ester
Rapeseed Methyl Ester
Palm Methyl Ester
Tallow Mthyl Ester
45.0(1) 51.9(9) 54.0(4) 58.0(17)
46.2(2) 48.0(10) 54.0(8) 62.9(13)
54.7(3) 54.4(11,12)
67.0(4) 49.9(13)
45.0(5) 54.5(14)
54.8(6) 54-65(15)
60.0(7) 61.2(6)
51.9(8) 61.8(16)
48.6(8)
(1)Reed, 1993 [48]; (2)Wagner et al., 1984 [49]; (3)McDonald et al., 1995[50]; (4)Pischinger et al., 1982[51];
(5)Peterson et al., 1994[52]; (6)Sharp, 1994[53]; (7)Midwest Biofuels, 1993 [54]; (8)Marchetti et al., (in
press)[55]; (9)Rakopoulos et al., 2006[56]; (10)McCormick, 2001[57]; (11)Van Gerpen et al., 2004[58];
(12)Wang et al., 2000[59]; (13)Kinast, 2003[60]; (14)Gragg, 1994[61]; (15)Peterson et al., 1993[62];
(16). Mittlebach et al., 1985[63]; (17) Schwab et al., 2000[64]
3.6. Cetane Number
Cetane number is defined as, “Number equal to the percentage by volume of cetane
added to basic diesel fuel to achieve specific ignition performance characteristics.” [24]. The
cetane number is one of the most commonly cited indicators of diesel fuel quality. It measures
the readiness of the fuel to autoignite when injected into the engine. It is generally dependent
on the composition of the fuel and can impact the engine's startability, noise level, and
exhaust emissions.
The cetane number of biodiesel is generally observed to be quite high. Data presented
below will show values varying between 45 and 67. In the United States, No. 2 diesel fuel
usually has a cetane number between 40 and 45. Table 11 shows the range of reported values
for the cetane number of four different types of biodiesel. The range of values for SME varies
from 45.0 to 67.0. The numbers in the brackets are the references from which the cetane
numbers were taken.
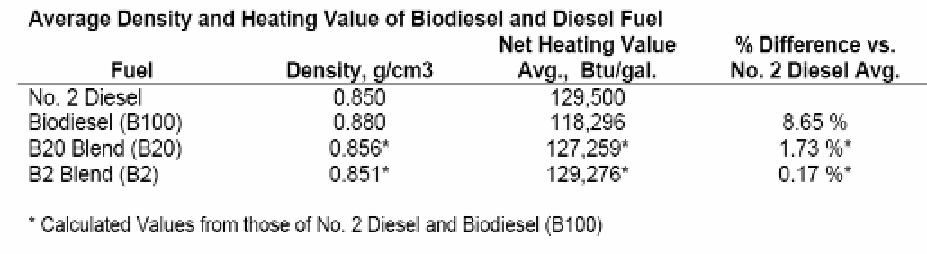
Table 12. Energy content in diesel and biodiesel